Word for Microsoft 365 Outlook for Microsoft 365 Word 2021 Outlook 2021 Word 2019 Outlook 2019 Word 2016 Outlook 2016 Word 2013 Outlook 2013 Word 2010 Outlook 2010 Word 2007 Outlook 2007 More…Less
To set or change table options in Word or Outlook, right-click a table and choose Table Properties.
Note: If you want to set properties for a particular row, column, or cell, click in that row, column, or cell before making changes in the Table Properties dialog box.
In this article
-
Table properties
-
Row properties
-
Column properties
-
Cell properties
-
Alt text
Table properties

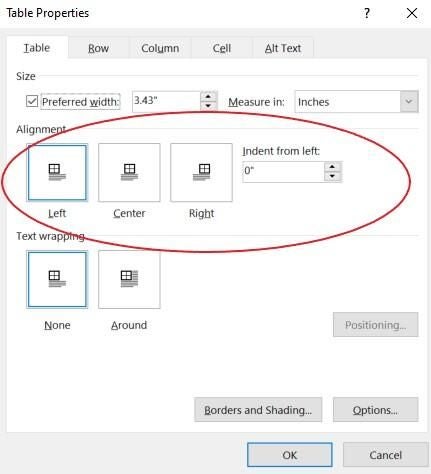
Click the Table tab to apply settings to your entire table:
-
Under Size, set the table’s overall width by selecting Preferred width and choosing a size. In the Measure in box, choose whether you want to measure the width in inches or a percentage of the page.
-
Under Alignment, choose whether you want to align your table to the left, center, or right of page. If you select Left, you can select an indentation distance in the Indent from Left box.
-
Under Text wrapping, select Around if you want nearby text on your page to wrap around your table; you can make text wrapping more precise by clicking Positioning, and then choosing options in the Table Positioning dialog box. If you don’t want text wrapping, select None.
-
Click Borders and Shading to change the border style, line color, and line width of your table.
-
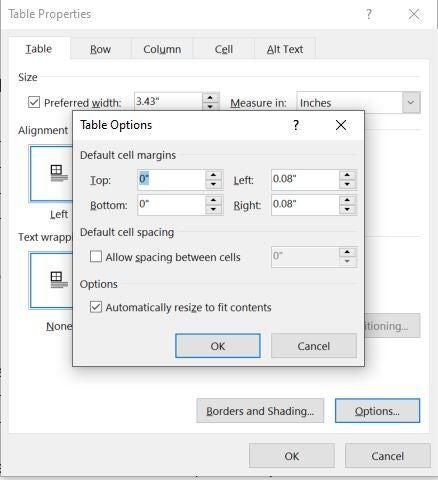
Click Options to set more table properties, including top and bottom cell margins, cell spacing, and automatic resizing of cell contents.
Top of Page
Row properties
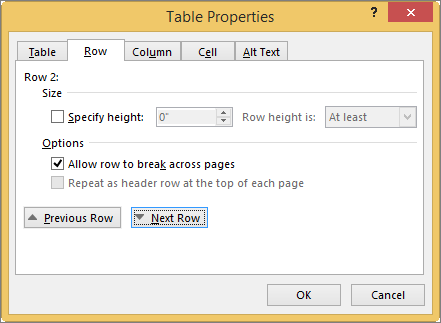
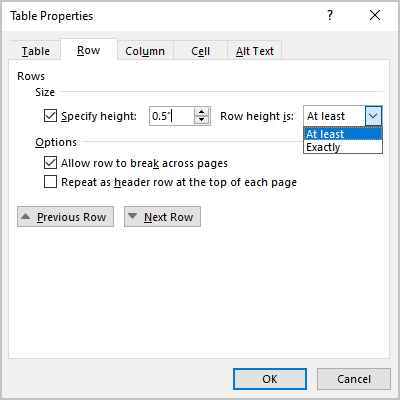
First, click in the row or select the rows you want to change, right-click, choose Table Properties, and then click the Row tab.
-
Under Size, set the row’s height by selecting Preferred height and choosing a size; you can further refine the height by selecting an option in the Row height is box.
-
Under Options, select options for breaking rows across pages or creating header rows.
-
To display the currently selected row at the top of the tab and navigate between rows without leaving the Table Properties dialog box, click Previous Row or Next Row.
Top of Page
Column properties
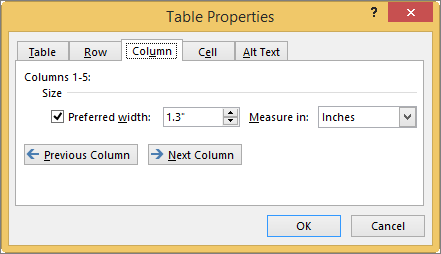
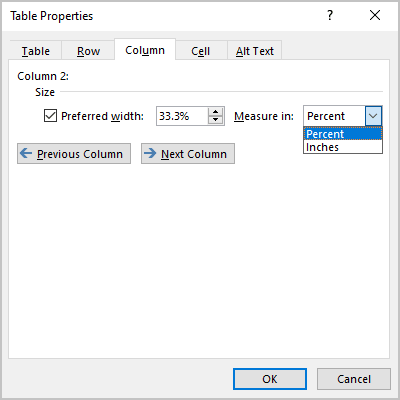
First, click in the column or select the columns you want to change, right-click, choose Table Properties, and then click the Column tab.
-
Under Size, set the column’s width by selecting Preferred width and choosing a size. In the Measure in box, choose whether you want to measure the width in inches or a percentage.
-
To display the currently selected column or columns at the top of the tab and navigate between columns without leaving the Table Properties dialog box, click Previous Column or Next Column.
Top of Page
Cell properties
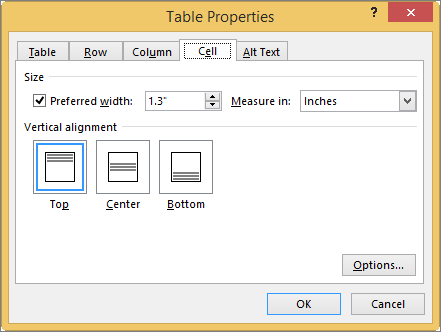
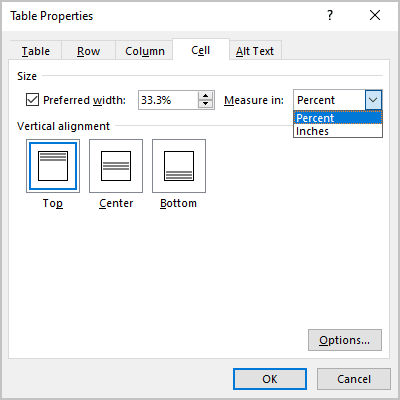
First, click in the cell that you want to change, right-click, choose Table Properties, and then click the Cell tab.
-
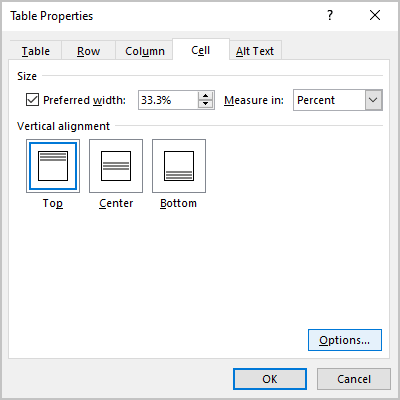
Under Size, set the cell’s width by selecting Preferred width and choosing a size. In the Measure in box, choose whether you want to measure the width in inches or a percentage.
-
Under Vertical alignment, choose an alignment option for the cell contents—Top (the default alignment), Center, or Bottom.
-
Click Options to set more cell properties, including top and bottom cell margins and text wrapping and fit options.
Top of Page
Alt text
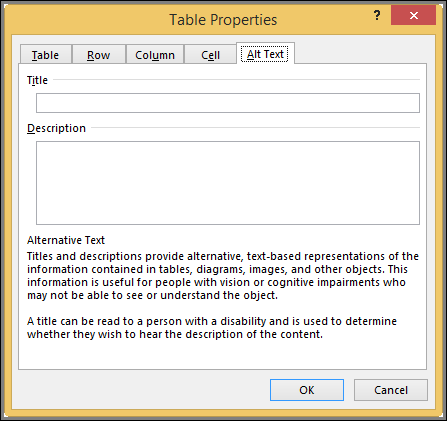
You can create alternative text (alt text) for your table to help people with screen readers understand the content of the table.
-
In the Description box, enter an explanation of the table.
-
In the Title box, enter a brief summary of the table.
Note: Unless you have a complex table, you will usually want to enter text in just the Description box. When you have complex content to describe, filling in the Title field is useful so that reading the full description is not necessary unless desired.
Top of Page
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
on
December 21, 2021, 7:41 AM PST
How to control a Word table’s horizontal alignment
When inserting a table in a Word document, you can stick with the default alignment or change it in any number of ways.
We may be compensated by vendors who appear on this page through methods such as affiliate links or sponsored partnerships. This may influence how and where their products appear on our site, but vendors cannot pay to influence the content of our reviews. For more info, visit our Terms of Use page.

Inserting a table in Microsoft Word is a simple task, but the default won’t always be exactly what you want. For instance, the default alignment is offset from the left margin. What if you want the table centered or even flush to the right margin? The good news is that realigning a table is easy. In this article, I’ll show you several ways to align a table the way you want.
I’m using Microsoft 365 on a Windows 10 64-bit system, but you can use earlier versions, and you can align tables in Word Online. You can work with your own file or download the demonstration .docx and .doc files.
SEE: Microsoft 365: A cheat sheet (free PDF) (TechRepublic)
The default table
When you insert a table or convert text into a table, Word positions it between the left and right margins (Figure A) – you can easily change this. And, there are several ways you can align a table across the horizontal plane between the left and right margins.
Figure A
The first thing you might want to change is the width. There’s not enough text to fill the cells, and it looks odd. In addition, the readability is low. Your eyes try to take in the entire table at once instead of reading the content. Fortunately, changing the width is easy.
- Click the table to select it. Doing so will display two handles (Figure B): one in the top-left corner and one in the bottom-right corner.
- Hover the mouse over the one at the bottom-right corner and your mouse will turn into a double-arrow.
- Simply drag up and to the left to decrease the width of the table and the width of each cell. Figure C shows the results.
Figure B
Figure C
The resized table is a better fit, and you could easily stop here, if you don’t want it aligned differently.
SEE: Checklist: Securing Windows 10 systems (TechRepublic Premium)
Alignment options
When you have a table that doesn’t spread from the left to the right margin, you might want to align it. You can apply specific alignments or indent the table.
You have three alignments: left, center and right. The default table is aligned to the left margin. You can easily check that by selecting the entire table (not a cell) and viewing the alignment options in the Paragraph group on the Home tab. Figure C (above) shows the Align Left option selected. To align the table, select the table and click one of the other options: Center or Left Align. Using these three options you can quickly and easily align your table to the left, center, or right of the page.
You can also use the Table Properties option to align a table. To access these options, right-click anywhere in the table and choose Table Properties from the resulting submenu. On the Table tab, choose an option from the Alignment section, and click OK. As you can see in Figure D, there are lots of properties, but we’re concerned with only those in the Alignment section. You might want to return later and review all the other options.
Figure D
The final alignment option is Indent From Left. This allows you to easily indent the table from the left margin. It’s the option to use if you need to be precise in that placement. You can do the same thing by dragging the table and using the ruler to snap the table into position (Figure E). Or use the Increase Indent option in the Paragraph group to move the table a half inch at a time.
Figure E
Aligning the content within each cell is just as easy using the Table Properties. On the Table tab, click the Options button to open the Table Options shown in Figure F. The Default Cell Margins section lets you change the size of all four margins. By default, the Automatically Resize To Fit Contents option is selected. To center or right align content in the cell, use the alignment options in the Paragraph group. However, you must select the text rather than the entire table; otherwise, clicking an option will align the table and not the content within the cells. Figure G shows the result of selecting the content (not the table) and clicking Right Align.
Figure F
Figure G
SEE: Windows 10: Lists of vocal commands for speech recognition and dictation (free PDF) (TechRepublic)
Word Online
Aligning is a bit different in Word Online, but still simple. With the table selected, right-click it and choose Paragraph Options. Use the Alignment dropdown in the General section. Using the Align options on the menu will align the text within the cells, not the table. So far, everything we’ve done has been clear cut, but you might have noticed that the text is positioned as a paragraph. The text doesn’t flow around the table.
Wrapping text
If you want text to wrap around the table, you need to change another default option. Go back to the Table Properties dialog. Below the alignment options, you’ll see the text wrapping options. The default is no wrapping. Simply click the Around option (Figure H) and click OK. As you can see, this option pulls up the text below and wraps it around the table. I clicked Backspace twice to pull the text up to align it with the top of the table. Pulling the text up this way may cause the paragraph to adopt some of the table’s properties. Simply click Normal to fix that.
Figure H
Stay tuned
Aligning Word tables as a whole is a simple task, and there are a number of ways to get the alignment you want. If you repeat this task often, you might want to change the default alignment; in a future article, I’ll show you how to do so.
Also See
-
How to use the many text wrapping options in Microsoft Word
(TechRepublic) -
How to make fewer mistakes and work more efficiently using predictive text in Microsoft 365
(TechRepublic) -
Google Workspace vs. Microsoft 365: A side-by-side analysis
(TechRepublic Premium) -
Must-read coverage: Windows 10
(TechRepublic on Flipboard)
-
Microsoft
-
Software
Right-click anywhere inside the table and then choose the “Table Properties” command from the context menu that appears. In the Table Properties window that opens, you can choose left, center, or right alignment by clicking those options in the “Alignment” section.
Contents
- 1 How do I align table margins in Word?
- 2 How do you center align a table horizontally in Word?
- 3 How do I fix misaligned tables in Word?
- 4 How do I fix the spacing between tables in Word?
- 5 How do you put a table in the center?
- 6 How do I align text in a table in Word 2019?
- 7 Why can’t I type above a table in Word?
- 8 How do you insert a space before a table in Word?
- 9 Why is there a gap in my Word table?
- 10 How do you change the alignment in Word?
- 11 Which command is used to align the table at the center of the document?
- 12 What is the command used to align the table at the center in LaTeX?
- 13 How do I center text in a table in CSS?
- 14 How do I align text in a table?
- 15 How do I center a table in Word 2020?
- 16 How do I reset my table of contents to default?
- 17 How do you sort a table in descending order in Word?
- 18 How do you start typing after a table in Word?
- 19 How do you type above a table in Word on a Mac?
- 20 How do you move a table in Word from the top of the page?
How do I align table margins in Word?
If you want to align the table borders with the outside text margins: – On the Table Tools > Layout tab of the ribbon, click the Cell Margins button. Change the left and right cell margins from the default 0.19 cm to 0.
How do you center align a table horizontally in Word?
Center a Table Horizontally in Word. Once you have selected the entire table, press “Ctrl” and “E” on the keyboard to center the table between the left and right margins.
How do I fix misaligned tables in Word?
Right-click anywhere inside the table and then choose the “Table Properties” command from the context menu that appears. In the Table Properties window that opens, you can choose left, center, or right alignment by clicking those options in the “Alignment” section.
How do I fix the spacing between tables in Word?
Follow these steps:
- Right-click anywhere within the table you want to format.
- Choose the Table Properties option from the Context menu.
- Make sure the Table tab is selected.
- Click on the Options button at the bottom of the dialog box.
- Make sure the Allow Spacing Between Cells check box is selected.
How do you put a table in the center?
One of the most common ways to center a table is to set both the bottom and top margins to 0, and the left and right margins to auto. If you’re after a table that’s an exact width, you may do this as you usually would and the automatic margin will divide the space left over.
How do I align text in a table in Word 2019?
Go to the Layout tab and you will find there’s an Alignment toolbox there. The Alignment toolbox has nine buttons for aligning text in a table in Microsoft Word. From left to right, and top to bottom, the buttons let you align text to the right, and top, center and top, and left and top.
Why can’t I type above a table in Word?
Press “Enter” if the table is at the top of the document; press “Ctrl-Shift-Enter” if the table is at the top of a section. In either case, this creates a blank line directly above the table.
How do you insert a space before a table in Word?
Follow these steps:
- Right-click on the table.
- Select Table Properties from the Context menu.
- Make sure the Table tab is displayed.
- In the Text Wrapping area, click the Around icon.
- Click the Positioning button.
- Adjust the Top and Bottom settings to reflect how much space you want left before and after the table.
Why is there a gap in my Word table?
1 The row height may exceed the space available on the preceding page. (Don’t specify row height.) 2 Text in the row may be set to keep with next. (Turn that off.)
How do you change the alignment in Word?
Press one of the shortcut keys to adjust the alignment of any highlighted text.
- For left alignment, highlight the text and press Ctrl + Shift + L .
- For center alignment, highlight the text and press Ctrl + Shift + E .
- For right alignment, highlight the text and press Ctrl + Shift + R .
Which command is used to align the table at the center of the document?
You can also enclose the tabular environment within a table environment. Not only will it allow you to center it (using the command centering ) but also to add a caption, a label for cross-reference, and to tweak the placement on the page.
What is the command used to align the table at the center in LaTeX?
The text of a figure or table can be centered on the page by putting a centering command at the beginning of the figure or table environment. Unlike the center environment, the centering command does not start a new paragraph; it simply changes how LaTeX formats paragraph units.
How do I center text in a table in CSS?
To center align text in table cells, use the CSS property text-align. The
tag align attribute was used before, but HTML5 deprecated the attribute. Do not use it. So, use CSS to align text in table cells.
How do I align text in a table?
Follow these steps to align text in a table:
- Select the cells, columns, or rows, with text that you want to align (or select your entire table).
- Go to the (Table Tools) Layout tab.
- Click an Align button (you may have to click the Alignment button first, depending on the size of your screen).
How do I center a table in Word 2020?
Centering a Table
- Right-click on the table. Word displays a Context menu.
- Choose Table Properties from the Context menu. Word displays the Table Properties dialog box.
- Make sure the Table tab is selected. (See Figure 1.)
- Click on Center.
- Click on Close.
How do I reset my table of contents to default?
Go to References again and click the Table of Contents button. You’ll now see the default TOC styles. Insert the TOC of your choosing. Done!
How do you sort a table in descending order in Word?
Sort a table in Word
- Select anywhere in the table.
- Select Table Tools Layout > Sort.
- Choose your sort criteria: Select the column you want to Sort by. To sort on a second column, select Then by and select another column. Select Ascending or Descending.
- Select OK.
How do you start typing after a table in Word?
- Add a new row to the table.
- Select the row (by clicking on the left side of the page or drag through the whole row)
- In Table Tools > Layout click on Convert To Text then OK.
How do you type above a table in Word on a Mac?
Press Ctrl+Home to place the insertion point in the leftmost cell of the first row. 2. Click on the Layout tab and then click on the Split Table button. Word will automatically create an empty paragraph above the table.
How do you move a table in Word from the top of the page?
- Click to place your cursor within the table.
- On the ribbon in the Table Tools Layout tab, click Properties in the Table group.
- On the Table tab, click Positioning to open the Table Positioning dialog box.
- In the Vertical section, click the Position drop down and select Top.
Cell Margins and Cell Spacing are two important settings in any Microsoft Word Table but they aren’t used much and not well understood.
Cell margins are the spaces between your text and the edge of the cell. They can be set separately for the top, bottom, and either side of the cells.
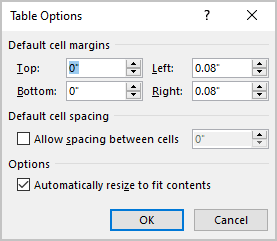
To change the cell margins, we again click in the table and go to the Layout tab on the right. Then click Cell Margins in the Alignment group.
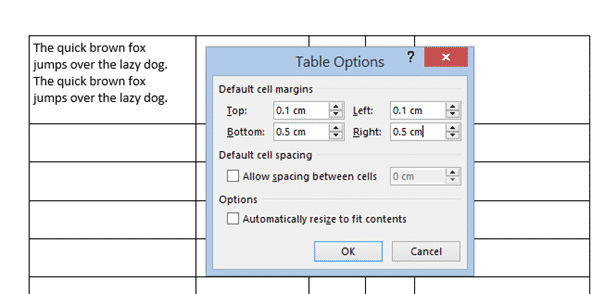
In the Table Options dialog that opens, use the spinners to incrementally change each of the four margins, or simply type in the margin that you want into each field; Top, Bottom, Left or Right.

The margins we’ve selected above are quite large, just to show you clearly how his setting changes your table. Here’s the large cell margins (left) compared to zero cell margins (right).

You can, of course have different margins on different sides:
Individual, Row or Column Cell Margins
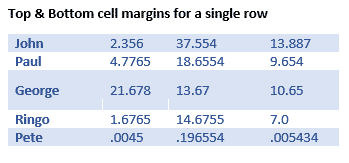
Table cell margins can be changed for a row, column or even a single cell, but it’s nowhere near the main Cell Margins ribbon button.
Select the column, row or cell you want to change then go to Table Layout | Table | Properties | Cell | Options. UNcheck the box ‘Same at the whole table’ then change the margin settings.

Here’s a single row, highlighted a little by increasing the top & bottom cell margins.
Why Adjust Table Cell Margins?
Cell margins are useful to separate lines in a table, especially when there’s no gridlines. Change the Top & Bottom cell margins to separate the lines and improve readability.

When space is tight, reducing the default left & right cell margins can help fit a table or contents into the available space.
Cell Spacing Tricks in Word Tables
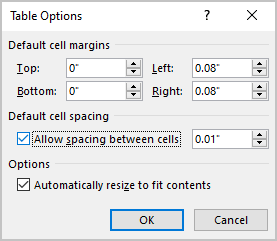
Word’s Table Options have an interesting choice, Cell Spacing. While cell margins are the space between the text and the edge of the cell, cell spacing puts space around each of the cells.
Cell spacing has a surprising effect on the look of a Word Table with single line borders.
Go to Table | Alignment | Cell Margins | Default cell spacing | Allow spacing between cells.
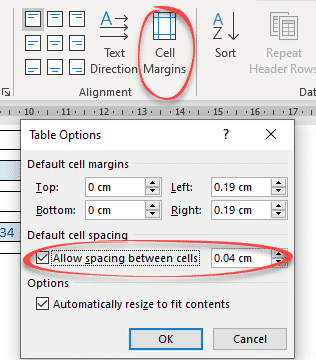
The default is OFF with no spacing.
Here’s how a Table looks using a standard single line border but increasing the cell spacing from the default, Zero.

Changes to Table Borders
As you can see, the single line table border becomes a twin gridline just by adding cell spacing to the same table.

Word table with Footnotes
Merge Cells in Word tables
Word tables for formatting magic
Indexing ‘bug’ in Word tables
After creating a table and filling it, the main task is to format the data and the table itself. The data in a table is formatted like any other text in Word by changing the font, aligning the text, etc.
A table is a collection of information or data, usually represented in horizontal rows and vertical columns. The box at the junction of each column and row is a cell that contains data such as text, numeric information, or images. You can select the cell, row, column, or entire table and apply formatting to the selected region.
Note that you can sort data in a table, perform calculations on numbers in a Word table, insert some formulas and functions. You can use a cell address to refer to a cell in the formula.
Select table elements
To select table a single cell:
- Using the mouse: Click the left edge of the cell:

- Using the keyboard: Position the cursor on the cell and select its content by pressing Shift+arrow (left or right).
To select multiple cells:
- Using the mouse: Click the left or right edge of the highest or lowest left cell in the range and move the mouse pointer diagonally to other cells to the right or left, down or up:
- Using the keyboard: Click the first cell you want to select, and then do one of the following:
- To select adjacent cells, hold down the Shift key, and click the last cell you want to select. The first, last, and all the cells in between will be selected.
- To select non-adjacent cells, hold down the Ctrl key, and click each additional cell you want to select. All the cells you clicked will be selected.
To select a single table column:
- Using the mouse: Click the column’s top gridline or top border:
- Using the keyboard: Point to the top of the column. When the cursor changes to a downward-pointing arrow, click the column.
To select multiple columns:
- Using the mouse: Click the column’s top gridline or top border and move the mouse pointer to the right or left.
- Using the keyboard: When the cursor changes to a downward-pointing arrow, click the first column. Then do one of the following:
- To select adjacent columns, hold down the Shift key, and then click to select the last column.
- To select non-adjacent columns, hold down the Ctrl key, and then click to select each additional column.
To select a single table row:
- Using the mouse: Click to the left of the row:
- Using the keyboard: Point to the left edge of the row. When the cursor changes to an upward-pointing arrow, click to select the row.
To select multiple rows:
- Using the mouse: Click to the left of the row and move the mouse pointer to the rows above or below.
- Using the keyboard: When the cursor changes to an upward-pointing arrow, click the first row. Then do one of the following:
- To select adjacent rows, hold down the Shift key, and then click to select the last row.
- To select non-adjacent rows, hold down the Ctrl key, and then click to select each additional row.
See also how to select the entire table.
Format table elements
After creating a table, you can format individual cells (spaces formed by the intersection of a row and a column) or entire rows and columns by aligning text in cells, resizing columns and rows, and adding borders, shading, or colors.
Merge and split cells
You can merge multiple cells into one cell that spans multiple columns or rows. For example, if you want to enter a heading for multiple table columns in the first row, you can merge cells in the first row (see example above).
To merge cells, select them and do one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Merge group, click the Merge Cells button:
- Right-click the selection and select Merge Cells in the popup menu:
In addition to merging multiple cells to create one cell, you can split one cell to create multiple cells.
To split the cell, select it, then do one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Merge group, click the Split Cells button:
- Right-click the selection and select Split Cells… in the popup menu:
Note: The Split Cells… item in the popup menu is displayed if only one cell is selected or the cursor is positioned inside the cell. If you select multiple cells, you won’t see Split Cells… in the popup menu.
In the Split Cells dialog box, specify the number of columns and rows created in place of the split cell:
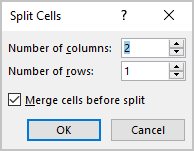
Note: If you select several cells, the Merge cells before split check box in the Split Cells dialog box is selected by default:
- The selected Merge cells before split check box to force Word to merge selected cells into one, then split that one cell into the specified number of rows and columns.
- The deselected Merge cells before split check box to force Word to split every cell into the specified number of rows and columns.
Resize a table and table elements
- Using the mouse:
To resize individual rows and columns, do one of the following:
- Hover your pointer over a row or column border until your pointer becomes two lines with two arrows:
Click and hold as you drag the border to resize the row or column.
- Drag the sliders in the Table Ruler to set to desired height and width. E.g.:
See how to resize an entire table.
- Hover your pointer over a row or column border until your pointer becomes two lines with two arrows:
- Using the keyboard:
- Select what you need to change:
- Position the cursor in a cell in the row or the column, or
- Select entire row or column, or multiple rows or columns.
- Do one of the following:
- On the Layout tab, in the Cell Size group, change the values in the Height and Width fields:
- Open the Table Properties dialog box by doing one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- Right-click the table and select Table Properties… in the popup menu:
In the Table Properties dialog box:
- On the Row tab, under Size, select the Specify height check box, then:
- In the Specify height field, type or select the value you need,
- In the Row height is dropdown list, select one of the items:
- At least to specify the minimal height,
- Exactly to fix the row height:
Note: To specify a height for other rows, click the Previous Row and Next Row buttons. Word highlights the appropriate row.
- On the Column tab, under Size, select the Preferred width check box, then:
- In the Preferred width field, type or select the value you need,
- In the Measure in dropdown list, select one of the items:
- Percent to specify the percentage of the table width,
- Inches to fix the column width:
Note: To specify a width for other columns, click the Previous Column and Next Column buttons. Word highlights the appropriate column.
- On the Cell tab, select the Preferred width check box to specify the width for the current column:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- On the Layout tab, in the Cell Size group, change the values in the Height and Width fields:
- Select what you need to change:
Note: See more about formatting a table.
Align text in a Word table cell
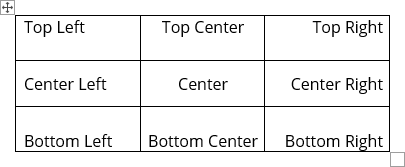
To align the text in one or more cells, select them, and then on the Table Layout tab, in the Alignment group, choose one of the nine proposed alignments:
- Align Top Left (the default alignment),
- Align Top Center,
- Align Top Right,
- Align Center Left,
- Align Center,
- Align Center Right,
- Align Bottom Left,
- Align Bottom Center,
- Align Bottom Right:
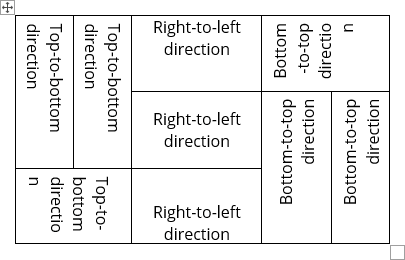
Modify text Direction
To change the text direction, select a cell or several cells, and then on the Table Layout tab, in the Alignment group, click the Text Direction button multiple times to cycle through the available directions:
Change the cell margins
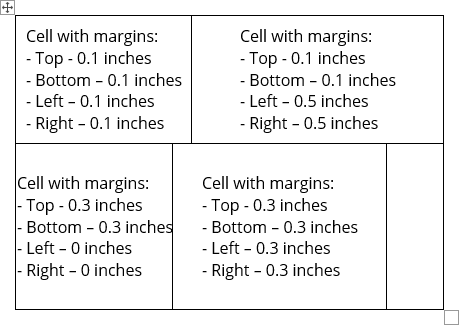
When you fill a table, you can change the cell spacing using the Paragraph options. Word offers the options to change the cell margins:
To customize cells margins, select a cell or several cells, then do one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Alignment group, click the Cell Margins button:
In the Table Options dialog box:
- To specify cell margins, in the Default cell margins section, type or select the values for Top, Bottom, Left, and Right margins:
- If you prefer to resize the table according to cell margins and specified spacing, leave the Automatically resize to fit contents check box selected.
If you prefer to leave the table without changes, clear the Automatically resize to fit contents check box.
- To specify cell margins, in the Default cell margins section, type or select the values for Top, Bottom, Left, and Right margins:
- Open the Table Properties dialog box.
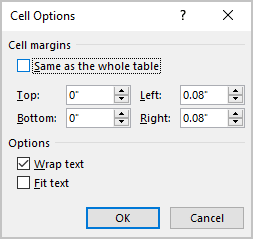
In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Cell tab, click the Options… button:
In the Cell Options dialog box:
- Clear the Same as the whole table check box,
- To specify cell margins, in the Default cell margins section, type or select the values for Top, Bottom, Left, and Right margins:
Change the space between cells
To increase or decrease the spacing between cells, select a cell or several cells, then do the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Alignment group, click the Cells Margins button:
In the Table Options dialog box:
- To specify the spacing between cells, in the Default cell spacing section, select the Allow spacing between cells check box, then type or select the value for spacing:
- If you prefer to resize the table according to cell margins and specified spacing, leave the Automatically resize to fit contents check box selected.
If you prefer to leave the table without changes, clear the Automatically resize to fit contents check box.
- To specify the spacing between cells, in the Default cell spacing section, select the Allow spacing between cells check box, then type or select the value for spacing:
For example, spacing between cells = 0.2 inches:
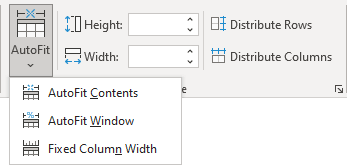
AutoFit features
After filling a table, editing the content, or inserting a text, it is possible to autoformat a table for the perfect look.
To use the Word AutoFit features, do the following:
1. Select a table.
2. On the Table Layout tab, in the Size group:
- To make all columns the same width, click the Distribute Columns button.
- To make each row the same height, click the Distribute Rows button.
- Click the AutoFit button, then choose one of the options:
- To fit the columns to the text (or page margins if cells are empty), select AutoFit Contents.
- To fit the table to the document content, select AutoFit Window.
- To keep Word from automatically adjusting the column size, select Fixed Column Width.