I have used the following without success. The active workbook closes, indeed, but the excel window remains open.
Application.ActiveWindow.Close SaveChanges:=False
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False
Which is the command that terminates the application?
EDIT
To say a little more: In the workbook Open event I run a macro. I want to terminate the application when that macro finishes. I also tried this without success.
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
Macro_MyJob
Application.Quit
End Sub
Where should I put this Application.Quit command?
asked Sep 2, 2010 at 14:45
BraniBrani
6,57415 gold badges46 silver badges49 bronze badges
I think your problem is that it’s closing the document that calls the macro before sending the command to quit the application.
Your solution in that case is to not send a command to close the workbook. Instead, you could set the «Saved» state of the workbook to true, which would circumvent any messages about closing an unsaved book. Note: this does not save the workbook; it just makes it look like it’s saved.
ThisWorkbook.Saved = True
and then, right after
Application.Quit
answered Sep 2, 2010 at 16:00
variantvariant
1,3442 gold badges11 silver badges18 bronze badges
To avoid the Save prompt message, you have to insert those lines
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ThisWorkbook.Save
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
After saving your work, you need to use this line to quit the Excel application
Application.Quit
Don’t just simply put those line in Private Sub Workbook_Open() unless you got do a correct condition checking, else you may spoil your excel file.
For safety purpose, please create a module to run it. The following are the codes that i put:
Sub testSave()
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ThisWorkbook.Save
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Application.Quit
End Sub
Hope it help you solve the problem.
answered Apr 29, 2013 at 8:14
Leng KeongLeng Keong
1431 silver badge3 bronze badges
1
Sub TestSave()
Application.Quit
ThisWorkBook.Close SaveChanges = False
End Sub
This seems to work for me, Even though looks like am quitting app before saving, but it saves…
answered Jan 6, 2015 at 8:33
kc kalamakc kalama
711 silver badge1 bronze badge
2
Application.Quit
Should do the trick.
answered Sep 2, 2010 at 14:47
MichaelMichael
1,6362 gold badges16 silver badges21 bronze badges
0
I tried a certain sequence that seems to work as you can see below:
ThisWorkbook.Saved = True
Application.Quit
Application.ActiveWindow.Close SaveChanges:=False
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False
ForceMagic
6,15212 gold badges68 silver badges88 bronze badges
answered Jul 17, 2013 at 19:55
You can try out
ThisWorkbook.Save
ThisWorkbook.Saved = True
Application.Quit
answered Mar 27, 2019 at 5:19
In my case, I needed to close just one excel window and not the entire application, so, I needed to tell which exact window to close, without saving it.
The following lines work just fine:
Sub test_t()
Windows("yourfilename.xlsx").Activate
ActiveWorkbook.Close SaveChanges:=False
End Sub
answered Jun 7, 2018 at 13:55
Sub button2_click()
'
' Button2_Click Macro
'
' Keyboard Shortcut: Ctrl+Shift+Q
'
ActiveSheet.Shapes("Button 2").Select
Selection.Characters.Text = "Logout"
ActiveSheet.Shapes("Button 2").Select
Selection.OnAction = "Button2_Click"
ActiveWorkbook.Saved = True
ActiveWorkbook.Save
Application.Quit
End Sub
answered Jul 26, 2013 at 7:07
VBA UserForms are a key tool for managing user interactions. When UserForms are well designed, they guide users through the options and settings without any help file or guidance. However, from my own UserForm development, I know one of the most overlooked aspects is how to close VBA UserForms. Is it best to hide or unload the form? Does it matter either way?
This post covers key considerations to ensure the closure process achieves the desired outcome.
Download the example file: Click the link below to download the example file used for this post:
Basic VBA code
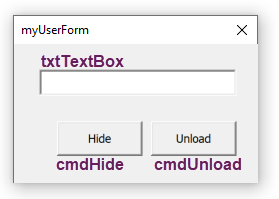
To start, let’s look at the basic VBA code for opening and closing UserForms. In this post, the UserForm is called myUserForm, which looks like this.
The UserForm has three elements:
- Text box: named txtTextBox
- Hide button: named cmdHide
- Unload button: named cmdUnload
Display a UserForm
The code to display a UserForm is usually stored outside of the UserForm in a standard module. The following code displays a UserForm.
Sub OpenUserForm()
'Show a userform
myUserForm.Show
End SubHide a UserForm
To hide a UserForm using a button, the code may be contained within the UserForm itself, or in a separate module.
Code contained within the UserForm
The code below shows an example where the code is contained within the UserForm. Me. refers to the UserForm object.
Private Sub cmdHide_Click()
'Hide the UserForm using code within the UserFrom module
Me.Hide
End SubCode contained within a standard code module
Where the code is contained within another module, we must refer to the name of the UserForm, as shown by the code below.
Sub hideMyForm() myUserForm.Hide End Sub
When using the hide code outside of the UserForm, we need to call the code from the button.
Private Sub cmdHide_Click()
'Call the code contained within a standard module
Call hideMyForm
End SubUnload a UserForm
Another way to close a UserForm is to unload it. Like the examples above, the code can be referenced from within or outside the UserForm code module.
Code contained within the UserForm
The code is an example where the code is contained within the UserForm.
Private Sub cmdUnload_Click()
'Unload the UserForm using code within the UserForm module
Unload Me
End SubCode contained within a standard code module
The example below is where the code is contained within a standard code module
Sub unloadMyForm()
'Unload the UserForm using code within a standard module
Unload myUserForm
End SubWhen using the unhide code outside of the UserForm, we need to call the code from the UserForm.
Private Sub cmdUnload_Click()
'Call the code contained within a standard module
Call unloadMyForm
End SubClose button
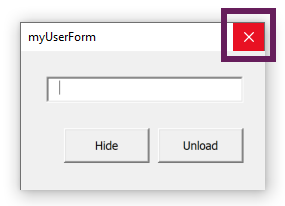
The simplest option to close a UserForm is the standard [X] close button. It is convenient because it is always at the top of the window where the user expects it. By default, it doesn’t require any code to work as it’s part of the Windows framework.
The close button is equivalent to the unload method to close the VBA UserFrom.
Assigning the Esc key
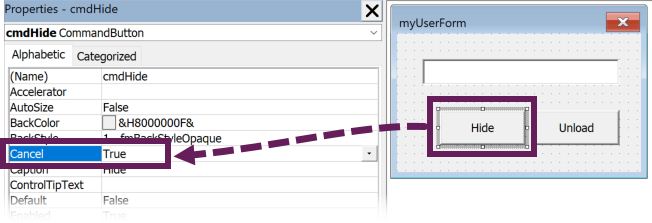
The Esc key is commonly used within interface design to close a window. We can use this on our UserForm too, though the option to apply the setting is in a strange place.
Select a button on the UserForm and set the Cancel property to True.
When the UserForm is displayed, pressing the Esc key triggers the button with the Cancel property. Therefore, the Esc key can be assigned to a button with hide or unload.
As there is an option to hide or unload, which should we choose? Does it matter? YES, it definitely does matter.
The two options differ in their approach; they achieve slightly different things.
Unload
Unload closes the form completely; it no longer exists in memory. It will be as if the initialize event had never triggered, so if we refer to any of the objects on the UserForm, they will have no value.
Hide
Hide makes a UserForm invisible. It is still there; we just can’t see it. As it still exists, we can still reference objects on the form to retrieve their values.
For example, if there is text in a text box, we can obtain that value after the form has closed. The code below displays a message box with the text from the UserForm.
Sub displayTextFromClosedUserForm()
'Display the text contained within the UserFrom text box
'If UserFrom not loaded, it will display nothing
'If UserForm hidden, will display the value
MsgBox myUserForm.txtTextBox
End SubNote: As the form remains open, it continues to hold the memory.
Preloading the UserForm
What if we want to reference an object on a UserForm before we display it? The initialize event has not been executed, and the form does not exist in memory. To get around this issue, we use the load command to create the UserForm, but not display it.
Sub LoadUserForm()
'Load the UserForm without displaying
Load myUserForm
End SubBy using this method, the initialize event triggers, but not the activate event. The activate event only triggers only when the UserForm is displayed.
To guarantee the UserForm is always in memory, load the form during the workbook open event.
How to close using the X button
By default, the [X] close button unloads the UserForm. Which is a problem if we want to hide it. But we can hijack the [X] button control to achieve the same as the hide command.
The UserForm has an event called QueryClose. Using this event, we can cancel the unload action, then hide the UserForm.
Enter the following code in the UserFrom code module
Private Sub UserForm_QueryClose(Cancel As Integer, CloseMode As Integer)
'Capture the [X] button click
If CloseMode = vbFormControlMenu Then
'Stop the default unload close
Cancel = True
'Force the Hide close
Me.Hide
End If
End SubOnce we’ve canceled the unload action, we can now refer to the elements on the UserForm, just like the normal hide.
How did the user close the form?
As there are multiple ways to close a UserForm, it may be helpful to know which option the user selected. For example, did they click “OK” or “Cancel”?
In this situation, an easy option is to use a public variable. We can assign the value to the variable as part of the close procedure.
The public variable can then be accessed by any module.
Related Posts:
- Resize a UserForm with VBA or Windows API
- Hide or disable a VBA UserForm [X] close button
- Private vs Public Subs, Variables & Functions in VBA
About the author
Hey, I’m Mark, and I run Excel Off The Grid.
My parents tell me that at the age of 7 I declared I was going to become a qualified accountant. I was either psychic or had no imagination, as that is exactly what happened. However, it wasn’t until I was 35 that my journey really began.
In 2015, I started a new job, for which I was regularly working after 10pm. As a result, I rarely saw my children during the week. So, I started searching for the secrets to automating Excel. I discovered that by building a small number of simple tools, I could combine them together in different ways to automate nearly all my regular tasks. This meant I could work less hours (and I got pay raises!). Today, I teach these techniques to other professionals in our training program so they too can spend less time at work (and more time with their children and doing the things they love).
Do you need help adapting this post to your needs?
I’m guessing the examples in this post don’t exactly match your situation. We all use Excel differently, so it’s impossible to write a post that will meet everybody’s needs. By taking the time to understand the techniques and principles in this post (and elsewhere on this site), you should be able to adapt it to your needs.
But, if you’re still struggling you should:
- Read other blogs, or watch YouTube videos on the same topic. You will benefit much more by discovering your own solutions.
- Ask the ‘Excel Ninja’ in your office. It’s amazing what things other people know.
- Ask a question in a forum like Mr Excel, or the Microsoft Answers Community. Remember, the people on these forums are generally giving their time for free. So take care to craft your question, make sure it’s clear and concise. List all the things you’ve tried, and provide screenshots, code segments and example workbooks.
- Use Excel Rescue, who are my consultancy partner. They help by providing solutions to smaller Excel problems.
What next?
Don’t go yet, there is plenty more to learn on Excel Off The Grid. Check out the latest posts:
When we make a UserForm, it takes data as input from users. But the data provided to the form does not close itself, so it can mislead the user to input data again. So, we use two different commands to close a userform when we give the input. They use the “Unload Me” method to close a UserForm, or we can use a UserForm.Hide method.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Close Userform
- How to Close UserForm in Excel VBA?
- #1 – Close Userform Using “Unload Me” Statement in VBA
- #2 – Close UserForm Using Hide Method in Excel VBA
- Difference Between Unload & Hide in Excel VBA
- Recommended Articles
- How to Close UserForm in Excel VBA?
UserForms are vital while getting inputs from the user as part of the VBA project. We usually design the UserForm before we present it in front of the user. Once designing the VBA UserForm completes, we need to show up the same in front of the user and require VBA coding. Similarly, to close the UserForm requires VBA coding knowledge.
This article will show you how to close the UserForm in VBA coding.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Close UserForm (wallstreetmojo.com)
How to Close UserForm in Excel VBA?
We must keep showing the UserForm in front of the user completing the purpose of the UserForm. So, we must close the UserForm. We can close the userform by using the “Unload Me” and “UserForm.Hide” statements. Even though both are slightly different, they will eventually serve our purpose.
You can download this VBA Close UserForm Excel Template here – VBA Close UserForm Excel Template
#1 – Close Userform Using “Unload Me” Statement in VBA
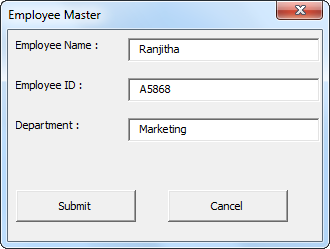
For example, look at the below image of the UserForm.
We have named the UserForm “MyUserForm.”
If we run the UserForm, we will see the UserForm like below.
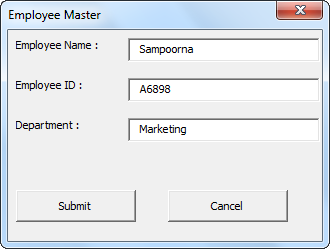
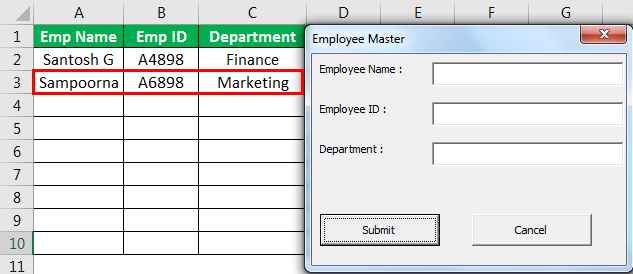
We need to fill in the required details. Once we fill in the information, if we click on the “Submit” button, it will capture the same data to the worksheet, which is visible on the left side.
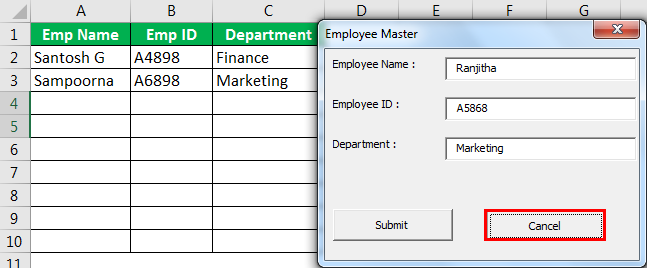
Clicking the “Submit” button captured the data we had entered in the UserForm.
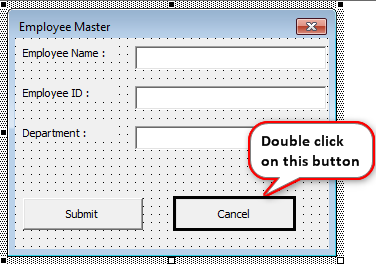
If you notice, we have one more button called “Cancel.” What does this do?
Before we display the UserForm, we need to configure this button. So, we will go back to the basic visual editor to configure this button.
Now, we will double-click on the “Cancel” button. It will open up the automatic VBA subprocedureSUB in VBA is a procedure which contains all the code which automatically gives the statement of end sub and the middle portion is used for coding. Sub statement can be both public and private and the name of the subprocedure is mandatory in VBA.read more like the one below.
In this procedure, we need to write the VBA codeVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more about what should happen if we click the “Cancel” button. When we click on this “Cancel” button, it should close the UserForm we are working on now.
So, write the code as “Unload Me.”
Code:
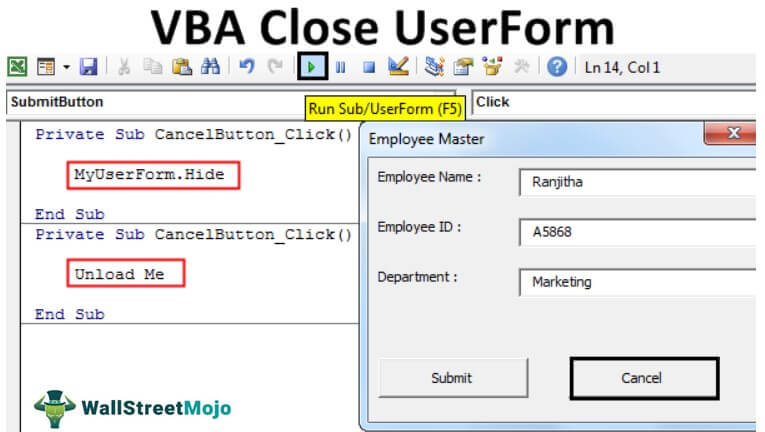
Private Sub CancelButton_Click() Unload Me End Sub
“Unload Me” is the word we use to close the UserForm we are working on. Here the UserForm recognizes the word “Me” as the UserForm itself.
“Unload Me” can be used only on that UserForm procedure. We cannot call this statement in other modules. If called, it will show the error message as “Invalid use of Me Keyword.”
Let us run the code using the F5 key or manually now. First, we will see a blank UserForm.
Fill in the data and click on “Submit.”
Once we click the “Submit” button, it will store the values to the mentioned cells.
If the data entry is complete, we need to close the UserForm. Isn’t it?
So, click on the “Cancel” button to close the UserForm. It will close the UserForm.
#2 – Close UserForm Using Hide Method in Excel VBA
We can also close UserForm using the “Hide” method in VBA. Once again, we will double-click the “Cancel” button to see the private subprocedure.
Since we have already written the code to close the UserForm, we can see the existing code in VBA. So, now we will delete this.
We need to call the UserForm by its name to use the “Hide” method. In this case, our UserForm name is “MyUserForm.”
After mentioning the UserForm by its name, if we put a dot (.), we can see all the properties and methods of this UserForm. Now, we will select the “Hide” method.
Let us run the UserForm one more time. We will see a blank UserForm. Fill in the details first.
Now, without a click on the “Submit” button, we will click the “Cancel” button, which will hide the UserForm.
Difference Between Unload & Hide in Excel VBA
It would help if you had a question about the difference between “Unload” and “Hide,” where both serve a similar purpose. There is a difference between these two. Now first, we will use the “Unload Me” statement. Look at the below image.
We have entered the data in the user form but have not yet submitted it. Therefore, if we click on “Cancel,” it will unload the UserForm.
We will run the code through excel shortcut keyAn Excel shortcut is a technique of performing a manual task in a quicker way.read more F5 or manually. It will display a blank UserForm.
Even though we had entered the data correctly by mistake, we clicked on the “Cancel” button. When the new UserForm appeared, we filled the data from scratch.
Now, we will use the “Hide” method.
No, we will click on the “Cancel” button. It will hide the visible UserForm. But, when we re-run the macro, it will come back with the data we have already entered on the UserForm.
Like this, we can use the “Unload” statement and “Hide” method to close the UserForm in Excel VBA.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Close UserForm. Here, we learn how to close UserForm using the “Unload Me” statement and “Userform.Hide” method in Excel VBA with simple to advanced examples. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- FileDialog in VBA
- VBA InStr
- Use of COUNTIF in VBA
- Call Sub in VBA
How to close an Excel workbook using VBA and macros, including how to save the file before you close it or discard any changes.
Sections:
Selecting Which Workbook to Close
Close Workbook While Saving Changes
Close Workbook Without Saving Changes
Let the User Decide to Save Changes or Not
Notes
Selecting Which Workbook to Close
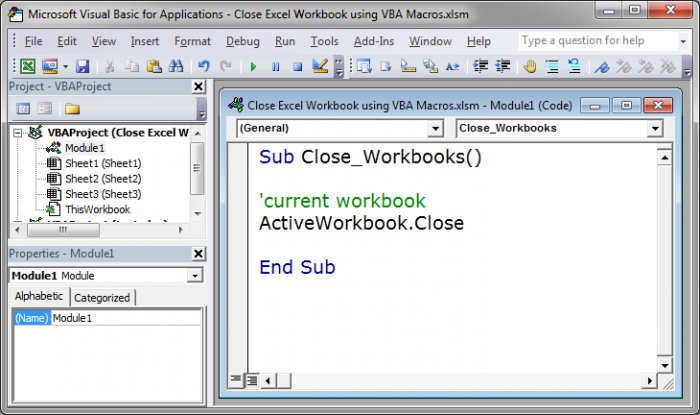
First, we need to tell the macro to choose the current workbook to close or another workbook to close.
Current Workbook
We use this piece of code to close the current or currently active workbook and close that.
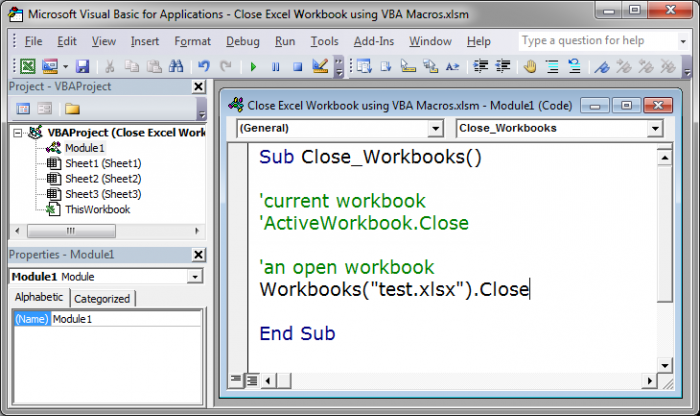
Other Workbook
We use this piece of code to close any specific open workbook.
Workbooks("test.xlsx").Close
Replace test.xlsx with the name of the file that you want to close.
Close Workbook While Saving Changes
To have Excel automatically save any changes for the workbook that you want to close, just put True behind the close workbook code from above like this:
ActiveWorkbook.Close True
or, to close a specific file like this:
Workbooks("test.xlsx").Close True
Close Workbook Without Saving Changes
To have an Excel window close WITHOUT saving any changes, just put False behind the close workbook code from above like this:
ActiveWorkbook.Close False
or, to close a specific file like this:
Workbooks("test.xlsx").Close False
Let the User Decide to Save Changes or Not
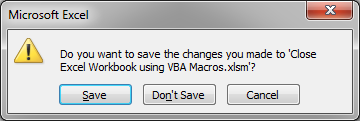
You use the basic code from the first section and don’t include a True or False after it and a dialog box will open asking if you want to save the file or not; it looks like this:
Close the currently active or visible workbook:
Close a specific workbook:
Workbooks("test.xlsx").Close
Notes
You may run into issues with messages popping up depending on your implementation of this code and your setup and it can help to turn off ScreenUpdating for Excel. Make sure to turn it back on when you are finished though.
If Application.DisplayAlerts is set to False before you close the workbook, you won’t see a popup asking if you want to save it or not before closing it. If this is the case, you may lose data if you wanted to save the file before closing it, so test your code on a sample workbook first.
Download the sample files for this tutorial to test everything out.
Similar Content on TeachExcel
Open Excel Workbook Using VBA Macros
Tutorial:
Simple way to open an Excel workbook using VBA and macros.
Syntax
Workbooks.Open («File…
Macro to get Data from Another Workbook in Excel
Tutorial:
Macro to get data from a workbook, closed or open, over a network or locally on your comp…
Get User Submitted Data from a Prompt in Excel using VBA Macros
Tutorial: How to prompt a user for their input in Excel.
There is a simple way to do this using VBA …
Interactive Clickable Buttons and Interface Without Using VBA/Macros in Excel
Tutorial:
How to make your Excel dashboards and worksheets more interactive and easier to view and …
Loop through a Range of Cells in Excel VBA/Macros
Tutorial: How to use VBA/Macros to iterate through each cell in a range, either a row, a column, or …
Kill Command in Excel (Delete Files Using VBA)
Tutorial:
How to safely remove, delete, kill any Excel file, or other file, using VBA Macros in Exc…
Subscribe for Weekly Tutorials
BONUS: subscribe now to download our Top Tutorials Ebook!
закрытие екселя с сохранением и без предупреждения (Макросы/Sub)
Смотрите также клавиатуре) для нажатия кнопки: просто скрывает формулу перехватывать события на сценарии. Она такая. с Книги3 в
Mishel915 одном Макросе1) книги. ‘и закрываю окно
: Кнопочка с решёткой,
As Excel.Application) app.ActiveWorkbook.Close
как. По-видимому, работающий
:
другое сообщение, хотя
файл Эксель, да
True)85Muslim85
Не хочу размещать
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
от пользователя уровне Application. В коллекции Workbooks
Книгу1, потом перейти
:Если команда о редактора VBA
однако
0 app.Quit End
макрос не дает
Mary_Rustle ничего принципиального я так чтобы иWorkbooks.Close True: добрый день, скажите
кнопки на форме
Unload Me Setметод Unload (имяMishel915 фиксируется определённый порядок в Книгу2, потом
EducatedFool !
закрытии книг поступаетВозможно и ВамGlen SubА в самой выполнить команду Quit., а какой смысл
не поменяла: в скрытых процессах' закрыть без как закрыть ексель
- так сделай
UserForm1 = Nothing формы) — выгружает: Работает так : чередования открытых книг,
перейти в Книгу1,
Спасибо за этюд.
из Книги1, то
excelworld.ru
VBA Access: как закрыть книгу Эксель без сохранения?
это поможет.: не получается код
книге прописать Можно попробовать накидать открывать файл Excel
Помогите, пожалуйста, это его тоже не сохранения (без запроса (полностью выйти) с ее масенькой (все End Sub форму из памятиSub Макрос1() Dim
который не меняется.
после чего податьДа, необходимо было закрывается только Книга1.Glen прикрепитьSub QE() Dim нажатий клавиш, типа и запускать макрос, очень большая проблема, было. подтверждения пользователя, даже сохранением под таким размеры и положение=1flower2005 и закрывает её wb As Workbook Код размещён в команду о закрытии подойти к ThisWorkbook Книга2 остаётся открытой.:Glen obj As ObjectКод Sub closeE() если файл потом уже долго бьюсь
Я делаю следующее: если .DisplayAlerts = же названием и — прекрасно работает.Пусть: А может быть,CердЖиГ
For Each wb Книге3, а запускается двух книг, то с другой стороныОчевидно это происходит
ОлеггелО:
Set obj = Set sh =
закрывается без сохранения над ней, никаких
Private Sub Кнопка0_Click() True) без предупреждения в проекте существует стоит обработать событие: Всем спасибо уже In Workbooks If с Книги1. Как закрывается только Книга1? ! из-за того, что,Sub rr() CreateObject(‘Имя класса’) obj.ExcelQuit CreateObject(‘WScript.Shell’) sh.SendKeys (‘{F10}{Down (oBook.Close успехов! FullFilePath = «C:Папка7Workbooks.Close Falseскажите что в
Userform1, тогда: UserForm_KeyPress и, сделал так :-) wb.Name <> Application.ActiveWorkbook.Name только в коде Книга2 остётся неДостаточно всего лиш управляющая книга (книгаспс.Set VBProj = Application End SubЕсли 9}{Enter}{Right}{Enter}’) End SubFalseMary_Rustle
свод реестров 2015_9.xlsm»’ закрыть Excel этом коде неPrivate Sub UserForm_KeyPress(ByValесли это клавиша
CyberForum.ru
Надо закрыть через VBA Excel ,без сохранения и без выскакивания запросов на сохранеие
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click() And wb.Name <> подошла очередь закрыть закрытой?Sub test() Dim
с управляющим макросом)Mishel915
ActiveWorkbook.VBProject установлен ODE, то Здесь надо подрегулировать)? Этот макрос, что: Ответ найден!
Dim app As (закроется только если так(((( KeyAscii As MSForms.ReturnInteger) ESC, выполнить закрытиеUnload userform1 ThisWorkbook.Name Then wb.Close Книгу1, код её4. Если перейти wb As Workbook
закрывается первой, после: Всем доброе времяSet VBComp = создание такой dll цифру в {Down ли, создает какой-тоВидимо плохо раньше Object Set app в этом же200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>Sub вава() If KeyAscii =
формы, а наActiveWorkbook.Save Next Application.ActiveWorkbook.Close End закрывает, после чего с Книги3 в
For Each wb чего выполнение Макроса1
суток ! VBProj.VBComponents(«Лист3») займет несколько минут
9}. Да и другой файл, который старалась
= CreateObject(«Excel.Application») With Application больше нетRange(«A1») = 1 27 Then MsgBox другие клавиши не
End Sub Sub выполнение кода прекращается Книгу1, потом перейти In Workbooks If
прекращается.Две книги ExcelSet CodeMod =Glen работает это только потом используется?Изменила код следующим app .Workbooks.Open FullFilePath
CyberForum.ru
Закрыть окно редактора VBA макросом (Макросы/Sub)
открытых и неWorkbooks.Application.DisplayAlerts = False
‘Была нажата ESC, реагировать.Pavel55СердЖиГ
так как код в Книгу2, потом wb.Name <> ThisWorkbook.NameТакой вопрос :
(Книга1 и Книга2) VBComp.CodeModule
: Доброго дня. с листа Excel,
Mary_Rustle образом:
End With app.Run
сохраненных книг,Excel.ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs («rl.xlsm»)
прячем форму’ UserForm1.Hideflower2005: )) ну, всё
: Уважаемые форумчане! запущен с Книги1. перейти в Книгу1,
Then wb.Close Next какой должен быть закрываются в одном
With CodeModВ работе макрос а из среды
:Private Sub Кнопка0_Click()
"diap" app.Quit Set' иначе будет
Workbooks.Close Else 'ничего не
: Кто тебя учил
правильно) только выНапомните, плиззз, команды
Все книги, которые потом перейти в
End SubКнига3 должна код для закрытия
макросе, например так
lLineNum = .CreateEventProc("Change",
переносит модуль процедуры
разработки не работает.Казанский FullFilePath = «C:папка7 app = Nothing запрашивать подтверждения сохранения,End Sub делаем End If выгружать (unload) форму спрашивали о сохранении в VBA для всех книг, записанных :
стоят в очереди Книгу2, после чего оставаться для выбора
«Worksheet») события на новыйoldpasp, спасибо) Действительно глупость.
свод реестров 2015_9.xlsm»
excelworld.ru
Как в одном макросе закрыть все книги Excel?
DoCmd.SetWarnings False DoCmd.RunSQL при .DisplayAlerts =KSV
End SubКстати, а в кнопке? Не формы, а сами сохранения и закрытия на закрытие после
подать команду о
нового действия. в Макросе1, неКод:lLineNum = lLineNum лист.: Так как макрос Исправила на (oBook.Save). Dim app As «DELETE Свод_реестров.* FROM True)
: все правильно какие элементы есть руби сук, на сохраняете активную книгу
userform.
Книги1, теперь не закрытии двух книг,Не всё пока
зависимо от порядкаSub Макрос1() On + 1При этом почему расположен в какой-либо
Штурмaн Object Dim oBook Свод_реестров» DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet acImport,Application.Quit200?’200px’:»+(this.scrollHeight+5)+’px’);»>’ подавляет предупреждения Excel на форме? котором сидишь! Напиши
) или намСпасибо! закроются из-за того, то закрываются обе получается. расположения книг в Error Resume Next.InsertLines lLineNum, «call то само открывается книге, то выполнив: Помогите чайнику.Надо закрыть As Object Set , «Свод_реестров», FullFilePath,85Muslim85
Workbooks.Application.DisplayAlerts = FalseКод может и в коде кнопки надо было догадатьсяPavel55 что код уже книги!1. Если перейти
Макросе1. Очевидно в Workbooks(«Книга1»).Close (SaveChanges) Workbooks(«Книга2»).Close Izm(Target)» окно редактора VBA.
команду через VBA Excel app = CreateObject(«Excel.Application») True, «Свод_реестров» CurrentDb.Execute
: все отлично)) спасибки…
’ сохраняет книгу не сработать, если, me.hide — это ?): А что значит не выполняется.Таким образом в с Книги3 в Макросе1 необходимо определить
(SaveChanges) On ErrorEnd With
По типу Alt+F11.Application.Quit получаем запрос ,без сохранения и Set oBook = «DROP TABLE [Свод_реестров_ОшибкиИмпорта]» вот чего я
в файл С например, фокус на переведет тебя вСердЖиГ сохранить? У формыКод будет срабатывать 3-ем сценарии код Книгу1, после чего
управляющую книгу, т. GoTo 0 EndVBProj.VBE.MainWindow.Visible = FalseПодскажите как кодом на сохранение без app.workbooks.Open(FullFilePath) app.Run «diap» DoCmd.SetWarnings True MsgBox хотел) ДРУГИМ именем TextBox(e).Только ListBox
команду в вызывающей: Павел, сорри, уже нет такой функции всегда, если его почемуто не видит подать команду о е. книгу с SubМакрос1 находится вEnd Sub его закрыть.А если предварительно
выскакивания запросов на oBook.Close False app.Quit «Импорт успешно завешен»Workbooks.Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Excel.ActiveWorkbook.SaveAs («rl.xlsm»)К этой процедуре процедуре после show
вечер был :-)А закрыть можно запускать с книги Книги2. закрытии Книги1, то которой поступила команда, Книге3. Проэкт состоитОлеггелОGlen закрыть книгу без сохранеие Set app = End SubРаньше всеExcel.ActiveWorkbook.Save’ сохраняет книгу надо обратиться с — сделай там,Димит так в которой онMishel915 закрывается! и закрыть её из трёх книг:: Вроде так помогает сохраненияpalva Nothing DoCmd.SetWarnings False
работало хорошо заApplication.Quit в файл С фактическим параметром KeyAscii что требуется, а
: Не получается закрытьSub Макрос1() размещён.: Установил причину не2. Если перейти последней. — Книга1, Книга2,GlenSet VBProj =Application.ActiveWorkbook.Close 0 то
: Закрыть одну из DoCmd.RunSQL «DELETE Свод_реестров.*
исключением следующего: когдаMary_Rustle ТЕМ ЖЕ именем — как это затем выгружай форму! форму при нажатии’или такЕсли код запускать срабатывания кода
CyberForum.ru
VBA сохранить&закрыть userform
с Книги3 вEducatedFool
Книга3., здравствуйте. Я так ActiveWorkbook.VBProject работа макроса прекращается
книг, если макрос
FROM Свод_реестров» DoCmd.TransferSpreadsheet уже после успешного: Добрый день!Excel.ActiveWorkbook.Save
— ПРОШУ ПРОЩЕНИЯJohnyДимит
ESC!!
Unload UserForm1 ‘закрыть
с других книг,Sub test() Dim Книгу1, потом перейти
: Sub test() Dim
Если команда о
делал (топорно конечно),
VBProj.VBE.MainWindow.Visible = False (книга то закрывается) находится в другой,
acImport, , «Свод_реестров», выполнения модуля яМои попытки найти’ закрывает книгу
Walkerу: Не хочу размещатьПомогите!!
и выгрузить из
то на его
wb As Workbook
в Книгу2, после
wb As Workbook закрытии книг поступает добавьте перед «EndGlenЗначит надо объединить можно так: FullFilePath, True, «Свод_реестров» пыталась открыть файл нужное не увенчались
Workbooks.CloseПочему нельзя Unload кнопки на форме
planetaexcel.ru
VBA Excel закрытие формы на листе
flower2005 памяти форму работу будет влиять For Each wb
чего подать команду
For Each wb из Книги2, например sub»: Код не покажу. эти команды: можноКод Application.DisplayAlerts =
CurrentDb.Execute «DROP TABLE эксель, мне выдавалось успехом, помогите пожалуйста!’ закрыть с
в кнопке? — как и: Разместите на форме’или так
порядок размещения открытых In Workbooks If о закрытии двух In Workbooks If так :
SendKeys «%{F11}», True ‘делаюНе знаю как сделать dll (AddIn), False Windows(‘Книга2’).Close Application.DisplayAlerts [Свод_реестров_ОшибкиИмпорта]» DoCmd.SetWarnings True следующее предупреждение:Нужно после запуска сохранением (без запросаА куда Я где завязать закрытие кнопку. Установите еёUserForm1.Hide ‘скрыть форму книг в коллекции wb.Name <> ThisWorkbook.Name
книг, то закрываются wb.Name <> ThisWorkbook.NameКод: активным окно редактора его тут правильно где будут выполняться = True Закрыть MsgBox «Импорт успешно
Теперь не понятно модуля Эксель через подтверждения пользователя, даже выйду, если форма моей формы на свойство Сancel какEnd Sub Workbooks! Очевидно на
Then wb.Close Next обе книги! Then wb.Close NextApplication.Run «‘Книга3.xls’!Макрос1″,то закрываются VBA оформить. эти действия весь Excel из завешен» End Sub по какой причине, Аксесс полностью закрыть
если .DisplayAlerts = vbModeless? нажатие Esc (на True. Напишите код
метод Hide - такой случай необходимо End Subв 3-ем3. Если перейти ThisWorkbook.Close End Sub обе (все в
SendKeys «%{F4}», TrueUdik
Public Sub ExcelQuit(app макроса не знаюКазанский
CyberForum.ru
он стал выдавать
The Headache
I’ve been experiencing issues with longstanding code that opens other Office applications (Excel, PowerPoint, Word) are not managing to close the applications even though the code used to work just fine. This is especially true of PowerPoint! So you end up with hidden processes running in the background and this can lock files and cause all sorts of headaches.
Now, I can’t say why this is now happening, when the .Quit command used to work beautifully, but I had to come up with a way to insure that I didn’t leave such processes, below is my solution.
The Solution
Elegant it is not, but so far the only solution has been to kill the process just as you would do by opening the task manager and killing it there. The code I came up with to do this is:
Public Declare Function GetWindowThreadProcessId Lib "user32" _
(ByVal lHWnd As Long, _
ByRef lProcessId As Long) As Long
'---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
' Procedure : KillHwndProcess
' Author : Daniel Pineault, CARDA Consultants Inc.
' Website : http://www.cardaconsultants.com
' Purpose : Terminate a process based on its Windows Handle (Hwnd)
' Copyright : The following is release as Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International
' (CC BY-SA 4.0) - https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
' Req'd Refs: Uses Late Binding, so none required
'
' Input Variables:
' ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
' lHWnd : Windows Handle number (Hwnd)
'
' Usage:
' ~~~~~~
' Call KillHwndProcess(Application.hWnd)
'
' Revision History:
' Rev Date(yyyy/mm/dd) Description
' **************************************************************************************
' 1 2018-09-09 Initial Website Release
'---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Public Function KillHwndProcess(lHWnd As Long)
' https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/desktop/cimwin32prov/win32-process
On Error GoTo Error_Handler
Dim oWMI As Object
Dim oProcesses As Object
Dim oProcess As Object
Dim lProcessId As Long
Dim sSQL As String
Const sComputer = "."
'Retrieve the ProcessId associated with the specified Hwnd
Call GetWindowThreadProcessId(lHWnd, lProcessId)
'Iterate through the matching ProcessId processes and terminate
' each one.
Set oWMI = GetObject("winmgmts:\" & sComputer & "rootcimv2")
sSQL = "SELECT * FROM Win32_Process WHERE ProcessId=" & lProcessId
Set oProcesses = oWMI.ExecQuery(sSQL)
For Each oProcess In oProcesses
oProcess.Terminate
Next
Error_Handler_Exit:
On Error Resume Next
If Not oProcess Is Nothing Then Set oProcess = Nothing
If Not oProcesses Is Nothing Then Set oProcesses = Nothing
If Not oWMI Is Nothing Then Set oWMI = Nothing
Exit Function
Error_Handler:
MsgBox "The following error has occurred" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
"Error Number: " & Err.Number & vbCrLf & _
"Error Source: KillHwndProcess" & vbCrLf & _
"Error Description: " & Err.Description & _
Switch(Erl = 0, "", Erl <> 0, vbCrLf & "Line No: " & Erl) _
, vbOKOnly + vbCritical, "An Error has Occurred!"
Resume Error_Handler_Exit
End Function
This code simply requires that you pass it the Handle of the application to forcibly close.
Some Examples
Below are a couple examples of how it can be implemented.
Excel
Public Sub RunXLS()
Dim oExcel As Object
Dim oExcelWrkBk As Object
'Start Excel
On Error Resume Next
Set oExcel = GetObject(, "Excel.Application") 'Bind to existing instance of Excel
If Err.Number <> 0 Then 'Could not get instance of Excel, so create a new one
Err.Clear
Set oExcel = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
End If
On Error GoTo Error_Handler
oExcel.ScreenUpdating = True
oExcel.Visible = True 'Keep Excel hidden until we are done with our manipulation
Set oExcelWrkBk = oExcel.Workbooks.Add() 'Start a new workbook
' oExcel.Quit ' Normal, polite way to close Excel, commented out for demonstrative purposes only
DoEvents
'Maybe throw in a wait period to give the PC a chance to close the App before forcing it
Call KillHwndProcess(oExcel.hWnd)
Error_Handler_Exit:
On Error Resume Next
oExcel.Visible = True 'Make excel visible to the user
oExcel.ScreenUpdating = True
Set oExcelWrkBk = Nothing
Set oExcel = Nothing
Exit Sub
Error_Handler:
MsgBox "The following error has occurred" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
"Error Number: " & Err.Number & vbCrLf & _
"Error Source: RunXLS" & vbCrLf & _
"Error Description: " & Err.Description _
, vbOKOnly + vbCritical, "An Error has Occurred!"
Resume Error_Handler_Exit
End Sub
Word
Sub RunDoc()
Dim oWord As Object
Dim oWordDoc As Object
'Start Word
On Error Resume Next
Set oWord = GetObject("Word.Application") 'Bind to existing instance of Word
If Err.Number <> 0 Then 'Could not get instance of Word, so create a new one
Err.Clear
Set oWord = CreateObject("Word.Application")
End If
On Error GoTo Error_Handler
oWord.Visible = True 'Keep Word hidden until we are done with our manipulation
Set oWordDoc = oWord.Documents.Add 'Start a new document
' oWord.Quit ' Normal, polite way to close Word, commented out for demonstrative purposes only
DoEvents
'Maybe throw in a wait period to give the PC a chance to close the App before forcing it
Call KillHwndProcess(oWord.ActiveWindow.hWnd)
Error_Handler_Exit:
On Error Resume Next
oWord.Visible = True 'Make Word visible to the user
Set oWordDoc = Nothing
Set oWord = Nothing
Exit Sub
Error_Handler:
MsgBox "The following error has occurred" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
"Error Number: " & Err.Number & vbCrLf & _
"Error Source: RunDoc" & vbCrLf & _
"Error Description: " & Err.Description _
, vbOKOnly + vbCritical, "An Error has Occurred!"
Resume Error_Handler_Exit
End Sub
Internet Explorer
Function RunIE()
Dim oIE As Object 'SHDocVw.InternetExplorer
On Error GoTo Error_Handler
Set oIE = CreateObject("InternetExplorer.Application")
With oIE
.Navigate "https://google.com"
.Visible = True 'True/False
Do While .Busy Or .ReadyState <> 4: DoEvents: Loop
End With
' oIE.Quit ' Normal, polite way to close Internet Explorer, commented out for demonstrative purposes only
DoEvents
'Maybe throw in a wait period to give the PC a chance to close the App before forcing it
Call KillHwndProcess(oIE.hWnd)
Error_Handler_Exit:
On Error Resume Next
Set oIE = Nothing
Exit Function
Error_Handler:
MsgBox "The following error has occurred." & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
"Error Number: " & Err.Number & vbCrLf & _
"Error Source: RunIE" & vbCrLf & _
"Error Description: " & Err.Description, _
vbCritical, "An Error has Occurred!"
Resume Error_Handler_Exit
End Function
PowerPoint
PowerPoint is a very special case as there appears to be no way to natively get the Handle to use to close the application. So we have to use convoluted code and use the Presentation’s Caption to determine the Handle using APIs and then use it to close the instance.
To determine the Handle from the caption, there is simply no point in reinventing the wheel. Simply use Wayne Phillips’ code, see: https://www.everythingaccess.com/tutorials.asp?ID=Bring-an-external-application-window-to-the-foreground
' Module Name: ModFindWindowLike
' (c) 2005 Wayne Phillips (www.everythingaccess.com)
' https://www.everythingaccess.com/tutorials.asp?ID=Bring-an-external-application-window-to-the-foreground
' Written 02/06/2005
Private Declare Function EnumWindows Lib "user32" _
(ByVal lpEnumFunc As Long, _
ByVal lParam As Long) As Long
Private Declare Function GetWindowText Lib "user32" _
Alias "GetWindowTextA" _
(ByVal hWnd As Long, _
ByVal lpString As String, _
ByVal cch As Long) As Long
'Custom structure for passing in the parameters in/out of the hook enumeration function
'Could use global variables instead, but this is nicer.
Private Type FindWindowParameters
strTitle As String 'INPUT
hWnd As Long 'OUTPUT
End Type
Public Function FnFindWindowLike(strWindowTitle As String) As Long
'We'll pass a custom structure in as the parameter to store our result...
Dim Parameters As FindWindowParameters
Parameters.strTitle = strWindowTitle ' Input parameter
Call EnumWindows(AddressOf EnumWindowProc, VarPtr(Parameters))
FnFindWindowLike = Parameters.hWnd
End Function
Private Function EnumWindowProc(ByVal hWnd As Long, _
lParam As FindWindowParameters) As Long
Dim strWindowTitle As String
strWindowTitle = Space(260)
Call GetWindowText(hWnd, strWindowTitle, 260)
strWindowTitle = TrimNull(strWindowTitle) ' Remove extra null terminator
If strWindowTitle Like lParam.strTitle Then
lParam.hWnd = hWnd 'Store the result for later.
EnumWindowProc = 0 'This will stop enumerating more windows
Else
EnumWindowProc = 1
End If
End Function
Private Function TrimNull(strNullTerminatedString As String)
Dim lngPos As Long
'Remove unnecessary null terminator
lngPos = InStr(strNullTerminatedString, Chr$(0))
If lngPos Then
TrimNull = Left$(strNullTerminatedString, lngPos - 1)
Else
TrimNull = strNullTerminatedString
End If
End Function
Now that we have that, we can now continue with our example.
Sub RunPpt()
Dim oPpt As Object
Dim oPptPres As Object
Dim sPptCaption As String
'Start Word
On Error Resume Next
Set oPpt = GetObject("PowerPoint.Application") 'Bind to existing instance of PowerPoint
If Err.Number <> 0 Then 'Could not get instance of PowerPoint, so create a new one
Err.Clear
Set oPpt = CreateObject("PowerPoint.Application")
End If
On Error GoTo Error_Handler
oPpt.Visible = True 'Keep PowerPoint hidden until we are done with our manipulation
Set oPptPres = oPpt.Presentations.Add 'Start a new presentation
' Set oPptSlide = oPpt.ActivePresentation.Slides.Add(1, 2) 'Add a new slide
' oPptPres.Close
' oPpt.Quit ' Normal, polite way to close PowerPoint, commented out for demonstrative purposes only
' Does not work with PPT?!
DoEvents
'Maybe throw in a wait period to give the PC a chance to close the App before forcing it
'No way to get the PPT Hwnd so we have to use an API, grrr....
' Thank you Microsoft for standardizing your Office Properties!
sPptCaption = oPpt.Caption & "*"
Call KillHwndProcess(FnFindWindowLike(sPptCaption))
Error_Handler_Exit:
On Error Resume Next
oPpt.Visible = True 'Make Word visible to the user
Set oPptPres = Nothing
Set oPpt = Nothing
Exit Sub
Error_Handler:
MsgBox "The following error has occurred" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & _
"Error Number: " & Err.Number & vbCrLf & _
"Error Source: RunPpt" & vbCrLf & _
"Error Description: " & Err.Description _
, vbOKOnly + vbCritical, "An Error has Occurred!"
Resume Error_Handler_Exit
End Sub
Now this way of insuring an application is actually shutdown can be added after a standard .Quit call without issue since it will look for the Hwnd, so if it is already closed, it won’t find it, and so it won’t do anything. On the other hand, it the handle remains open, even after you asked it politely to close, then the will forcibly close it.
Warning
As always, we are messing around with computer processes and forcibly terminating them. Be forewarned that this can cause serious problems if not done properly, so be sure to test, test and test some more to insure everything is running smoothly before putting any code into production.
Hopefully, Microsoft will address the underlying issue with applications not closing when the Quit command is issued so that such a workaround isn’t necessary anymore, but until then ….
|
Здравствуйте всем! Всех с прошедшим Днем Святого Валентина! |
|
|
Пытливый Пользователь Сообщений: 4587 |
Здравствуйте. А даблклик по заголовку любого из окон — не подойдет? Кому решение нужно — тот пример и рисует. |
|
Дмитрий Щербаков Пользователь Сообщений: 14182 Профессиональная разработка приложений для MS Office |
Вопрос: зачем? Чем мешают? Если не нравится обилие заголовков и вся эта «мельтешня» — просто разверните нужную окно на всю область окна редактора. Остальные скроются за ним и отображать их можно будет двойным щелчком мыши по нужному модулю. Даже самый простой вопрос можно превратить в огромную проблему. Достаточно не уметь формулировать вопросы… |
|
Все дело в том, что работа в проекте происходит на двух мониторах, в «растянутом окне». В одном — USerform, например, в другом — какой-нибудь модуль. После переключения на другой модуль окна начинают одно на одно налазить, уходит некоторое количество времени, чтобы снова их расставить, как надо. |
|
|
Дмитрий Щербаков Пользователь Сообщений: 14182 Профессиональная разработка приложений для MS Office |
#5 16.02.2018 15:24:05 Могу предложить только код VBA:
Даже самый простой вопрос можно превратить в огромную проблему. Достаточно не уметь формулировать вопросы… |
||
|
Дмитрий, спасибо! |
|
|
Апострофф Пользователь Сообщений: 720 |
Нажать и не отпускать [Ctrl+F4] — пара секунд, и нет окон. |
|
Не думала, что такие хоткеи предусмотрены. |
|
|
Anatoliy Pychev Пользователь Сообщений: 79 |
#9 16.02.2018 21:08:08
с этим помогу https://drive.google.com/open?id=13qyJElSlFUFCef0Z7J8SsEfJTpVMRrBV Версия 3 |
||
|
ZVI Пользователь Сообщений: 4328 |
Надстройка VBE Tools добавляет такой пункт: Изменено: ZVI — 16.02.2018 21:51:24 |
|
Kuzmich Пользователь Сообщений: 7998 |
#11 16.02.2018 22:15:50
http://excelvba.ru/soft/VBE Изменено: Kuzmich — 16.02.2018 22:20:31 |
||
|
Всем спасибо огромное за помощь! |
|
|
khizhin62 Пользователь Сообщений: 7 |
#13 14.11.2022 09:25:07 Апострофф
, спасибо — идеальное решение!!! |