Создание нового документа Word или открытие существующего из кода VBA Excel. Методы Documents.Add и Documents.Open. Сохранение и закрытие документа.
Работа с Word из кода VBA Excel
Часть 2. Создание и открытие документов Word
[Часть 1] [Часть 2] [Часть 3] [Часть 4] [Часть 5] [Часть 6]
Новый документ Word создается из кода VBA Excel с помощью метода Documents.Add:
|
Sub Test1() Dim myWord As New Word.Application Dim myDocument As Word.Document Set myDocument = myWord.Documents.Add myWord.Visible = True End Sub |
Переменную myDocument можно объявить с типом Object, но тогда не будет ранней привязки к типу Word.Document и подсказок при написании кода (Auto List Members).
Открытие существующего документа
Существующий документ Word открывается из кода VBA Excel с помощью метода Documents.Open:
|
Sub Test2() Dim myWord As New Word.Application Dim myDocument As Word.Document Set myDocument = _ myWord.Documents.Open(«C:Документ1.docx») myWord.Visible = True End Sub |
Замените в этой процедуре строку «C:Документ1.docx» на адрес своего файла.
Подключение к открытому документу
Присвоение переменной ссылки на существующий экземпляр Word.Application осуществляется в VBA Excel с помощью функции GetObject:
|
Sub Test3() Dim myWord As Object, myDoc As Word.Document On Error GoTo Instr Set myWord = GetObject(, «Word.Application») Set myDoc = myWord.Documents(«Документ1.docx») myDoc.Range.InsertAfter «Добавляем новый текст, подтверждающий подключение к открытому документу.» Exit Sub Instr: MsgBox «Произошла ошибка: « & Err.Description End Sub |
Если открытого приложения Word нет, выполнение функции GetObject приведет к ошибке. Также произойдет ошибка, если не будет найден указанный документ (в примере — «Документ1.docx»).
Сохранение и закрытие документа
Сохранение нового документа
Чтобы сохранить из кода VBA Excel новый документ Word, используйте метод SaveAs2 объекта Document:
|
myDocument.SaveAs2 («C:Документ2.docx») |
Замените «C:Документ2.docx» на путь к нужному каталогу с именем файла, под которым вы хотите сохранить новый документ.
Сохранение изменений в открытом документа
Сохраняйте изменения в существующем документе с помощью метода Document.Save или параметра SaveChanges метода Document.Close:
|
‘Сохранение изменений документа myDocument.Save ‘Сохранение изменений документа ‘при закрытии myDocument.Close ‘по умолчанию True myDocument.Close True myDocument.Close wdSaveChanges ‘Закрытие документа без ‘сохранения изменений myDocument.Close False myDocument.Close wdDoNotSaveChanges |
Закрытие любого сохраненного документа
Метод Document.Close закрывает документ, но не приложение. Если работа с приложением закончена, оно закрывается с помощью метода Application.Quit.
| title | keywords | f1_keywords | ms.prod | api_name | ms.assetid | ms.date | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Document.New event (Word) |
vbawd10.chm4001004 |
vbawd10.chm4001004 |
word |
Word.Document.New |
c37f7e20-f429-e921-3d17-609d536e8baa |
06/08/2017 |
medium |
Document.New event (Word)
Occurs when a new document based on the template is created. A procedure for the New event will run only if it is stored in a template.
Syntax
expression.**Private Sub Document_New’
expression A variable that represents a Document object.
Remarks
For information about using events with the Document object, see Using events with the Document object.
Example
This example asks the user whether to save all other open documents when a new document based on the template is created. (This procedure is stored in the ThisDocument class module of a template, not a document.)
Private Sub Document_New() Dim intResponse As Integer Dim strName As String Dim docLoop As Document intResponse = MsgBox("Save all other documents?", vbYesNo) If intResponse = vbYes Then strName = ActiveDocument.Name For Each docLoop In Application.Documents With docLoop If .Name <> strName Then .Save End If End With Next docLoop End If End Sub
See also
Document Object
[!includeSupport and feedback]
Using Excel VBA to create Microsoft Word documents
In these examples, we generate Microsoft Word Documents with various formatting features using
the Microsoft Excel VBA scripting language. These techniques can have many useful applications.
For instance if you have a list of data like a price or product list in Excel that you want to present
in a formatted Word Document, these techniques can prove useful.
In these examples, we assume the reader has at least basic knowledge of VBA, so we will not
go over basics of creating and running scripts. This code has been tested on Microsoft Word and Excel
2007. Some changes may be required for other versions of Word and Excel.
Writing to Word
Inserting a Table of Contents
Inserting Tabs
Inserting Tables
Inserting Bullet List
more on Inserting Tables
Multiple Features
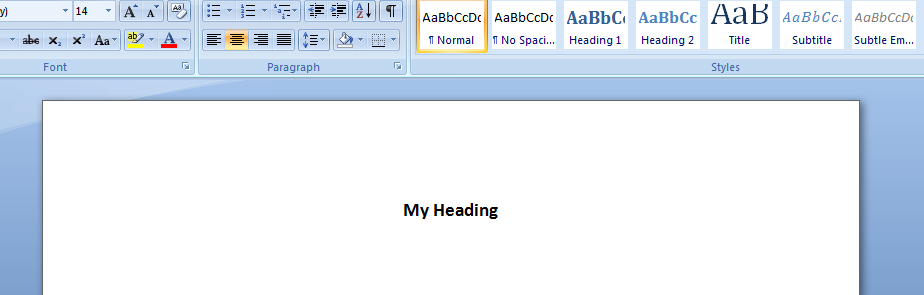
Function that demonstrates VBA writing to a Microsoft Word document
The following code illustrates the use of VBA Word.Application object and related properties.
In this example, we create a new Word Document add some text.
'In Tools > References, add reference to "Microsoft Word XX.X Object Library" before running.
'Early Binding
Dim wdApp As Word.Application
Set wdApp = New Word.Application
'Alternatively, we can use Late Binding
'Dim wdApp As Object
'Set wdApp = CreateObject("word.Application")
With wdApp
.Visible = True
.Activate
.Documents.Add
With .Selection
.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = wdAlignParagraphCenter
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Name = "arial"
.Font.Size = 14
.TypeText ("My Heading")
.TypeParagraph
End With
End With
Some VBA Vocabulary
ParagraphFormat
Represents all the formatting for a paragraph.
output in MS Word:
Inserting a Table of Contents into Word Document using Excel VBA
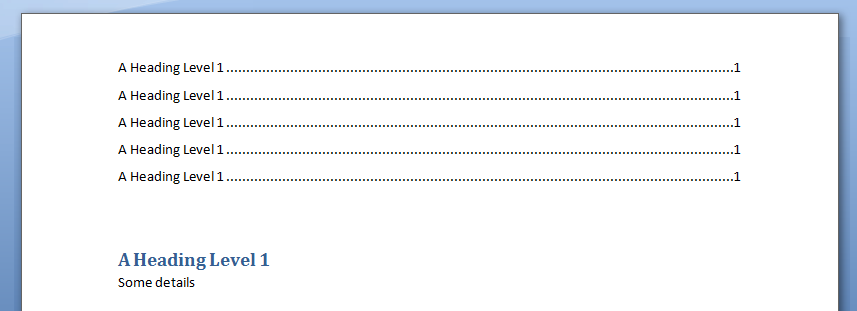
In this example, we generate a Table of Contents into a Word Document using Excel VBA
Sub sAddTableOfContents()
Dim wdApp As Word.Application
Set wdApp = New Word.Application
'Alternatively, we can use Late Binding
'Dim wdApp As Object
'Set wdApp = CreateObject("word.Application")
Dim wdDoc As Word.Document
Set wdDoc = wdApp.Documents.Add
' Note we define a Word.range, as the default range wouled be an Excel range!
Dim myWordRange As Word.range
Dim Counter As Integer
wdApp.Visible = True
wdApp.Activate
'Insert Some Headers
With wdApp
For Counter = 1 To 5
.Selection.TypeParagraph
.Selection.Style = "Heading 1"
.Selection.TypeText "A Heading Level 1"
.Selection.TypeParagraph
.Selection.TypeText "Some details"
Next
End With
' We want to put table of contents at the top of the page
Set myWordRange = wdApp.ActiveDocument.range(0, 0)
wdApp.ActiveDocument.TablesOfContents.Add _
range:=myWordRange, _
UseFields:=False, _
UseHeadingStyles:=True, _
LowerHeadingLevel:=3, _
UpperHeadingLevel:=1
End Sub
Some VBA Vocabulary
ActiveDocument.TablesOfContents.Add
The TablesOfContents property to return the TablesOfContents collection.
Use the Add method to add a table of contents to a document.
Some TablesOfContents Parameters
Range The range where you want the table of contents to appear. The table of contents replaces the range, if the range isn’t collapsed.
UseHeadingStyles True to use built-in heading styles to create the table of contents. The default value is True.
UpperHeadingLevel The starting heading level for the table of contents. Corresponds to the starting value used with the o switch for a Table of Contents (TOC) field. The default value is 1.
LowerHeadingLevel The ending heading level for the table of contents. Corresponds to the ending value used with the o switch for a Table of Contents (TOC) field. The default value is 9.
output Word Table in MS Word:
Write Microsoft Word Tabs
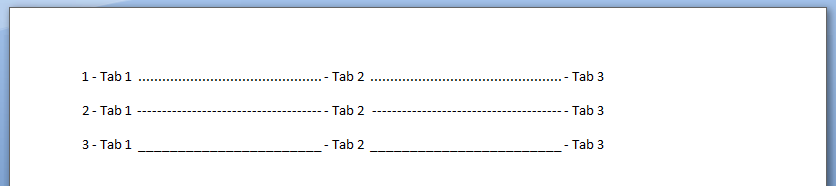
A function that writes tabbed content to a Microsoft Word Document. Note in each iteration, we change the
value of the leader character (characters that are inserted in the otherwise blank area created by the tab).
Public Sub sWriteMicrosoftTabs()
'In Tools > References, add reference to "Microsoft Word XX.X Object Library" before running.
'Early Binding
Dim wdApp As Word.Application
Set wdApp = New Word.Application
'Alternatively, we can use Late Binding
'Dim wdApp As Object
'Set wdApp = CreateObject("word.Application")
With wdApp
.Visible = True
.Activate
.Documents.Add
For Counter = 1 To 3
.Selection.TypeText Text:=Counter & " - Tab 1 "
' position to 2.5 inches
.Selection.Paragraphs.TabStops.Add Position:=Application.InchesToPoints(2.5), _
Leader:=Counter, Alignment:=wdAlignTabLeft
.Selection.TypeText Text:=vbTab & " - Tab 2 "
' position to 5 inches
.Selection.Paragraphs.TabStops.Add Position:=Application.InchesToPoints(5), _
Leader:=Counter, Alignment:=wdAlignTabLeft
.Selection.TypeText Text:=vbTab & " - Tab 3 "
.Selection.TypeParagraph
Next Counter
End With
End Sub
Some VBA Vocabulary
.TabStops.Add Use the TabStops property to return the TabStops collection. In the example above,
nprogram adds a tab stop positioned at 0, 2.5 and 5 inches.
output in MS Word:
Write Microsoft Word Tables
In this example, we generate a Microsoft Table using Excel VBA
Sub sWriteMSWordTable ()
'In Tools > References, add reference to "Microsoft Word XX.X Object Library" before running.
'Early Binding
Dim wdApp As Word.Application
Set wdApp = New Word.Application
'Alternatively, we can use Late Binding
'Dim wdApp As Object
'Set wdApp = CreateObject("word.Application")
With wdApp
.Visible = True
.Activate
.Documents.Add
With .Selection
.Tables.Add _
Range:=wdApp.Selection.Range, _
NumRows:=1, NumColumns:=3, _
DefaultTableBehavior:=wdWord9TableBehavior, _
AutoFitBehavior:=wdAutoFitContent
For counter = 1 To 12
.TypeText Text:="Cell " & counter
If counter <> 12 Then
.MoveRight Unit:=wdCell
End If
Next
End With
End With
End Sub
Some VBA vocabulary
Table.AddTable object that represents a new, blank table added to a document.
Table.Add properties
Range The range where you want the table to appear. The table replaces the range, if the range isn’t collapsed.
NumRows The number of rows you want to include in the table.
NumColumns The number of columns you want to include in the table.
DefaultTableBehavior Sets a value that specifies whether Microsoft Word automatically resizes cells in tables to fit the cells� contents (AutoFit). Can be either of the following constants: wdWord8TableBehavior (AutoFit disabled) or wdWord9TableBehavior (AutoFit enabled). The default constant is wdWord8TableBehavior.
AutoFitBehavior Sets the AutoFit rules for how Word sizes tables. Can be one of the WdAutoFitBehavior constants.
output in MS Word:
Write Microsoft Word bullet list
In this example, we write with bullet list and outline numbers with Excel VBA
'In Tools > References, add reference to "Microsoft Word XX.X Object Library" before running.
'Early Binding
Dim wdApp As Word.Application
Set wdApp = New Word.Application
'Alternatively, we can use Late Binding
'Dim wdApp As Object
'Set wdApp = CreateObject("word.Application")
With wdApp
.Visible = True
.Activate
.Documents.Add
' turn on bullets
.ListGalleries(wdBulletGallery).ListTemplates(1).Name = ""
.Selection.Range.ListFormat.ApplyListTemplate ListTemplate:=.ListGalleries(wdBulletGallery).ListTemplates(1), _
continuepreviouslist:=False, applyto:=wdListApplyToWholeList, defaultlistbehavior:=wdWord9ListBehavior
With .Selection
.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = wdAlignParagraphLeft
.Font.Bold = False
.Font.Name = "Century Gothic"
.Font.Size = 12
.TypeText ("some details")
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText ("some details")
.TypeParagraph
End With
' turn off bullets
.Selection.Range.ListFormat.RemoveNumbers wdBulletGallery
With .Selection
.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = wdAlignParagraphLeft
.TypeText ("some details")
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText ("some details")
.TypeParagraph
End With
' turn on outline numbers
.ListGalleries(wdOutlineNumberGallery).ListTemplates(1).Name = ""
.Selection.Range.ListFormat.ApplyListTemplate ListTemplate:=.ListGalleries(wdOutlineNumberGallery).ListTemplates(1), _
continuepreviouslist:=False, applyto:=wdListApplyToWholeList, defaultlistbehavior:=wdWord9ListBehavior
With .Selection
.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = wdAlignParagraphLeft
.TypeText ("some details")
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText ("some details")
End With
End With
output in MS Word:
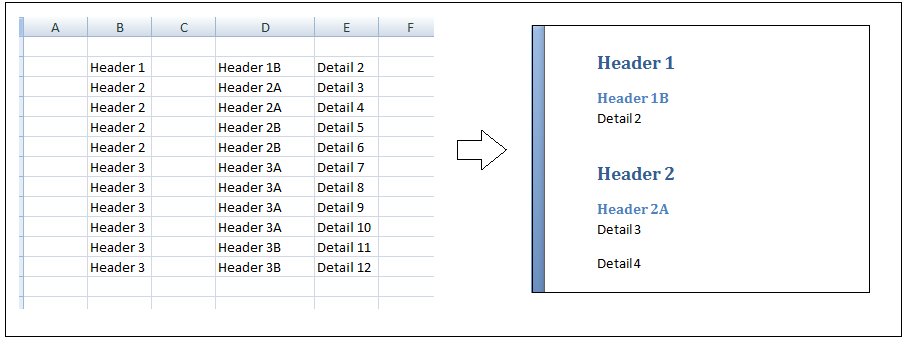
Another example of Writing Tables to Microsoft Word
In this example we will create a word document with 20 paragraphs. Each paragraph will have a header with a header style element
'In Tools > References, add reference to "Microsoft Word XX.X Object Library" before running.
Dim wdApp As Word.Application
Dim wdDoc As Word.Document
Set wdApp = New Word.Application
wdApp.Visible = True
Dim x As Integer
Dim y As Integer
wdApp.Visible = True
wdApp.Activate
wdApp.Documents.Add
wdApp.ActiveDocument.Tables.Add Range:=wdApp.Selection.Range, NumRows:=2, NumColumns:= _
2, DefaultTableBehavior:=wdWord9TableBehavior, AutoFitBehavior:= _
wdAutoFitFixed
With wdApp.Selection.Tables(1)
If .Style <> "Table Grid" Then
.Style = "Table Grid"
End If
.ApplyStyleHeadingRows = True
.ApplyStyleLastRow = False
.ApplyStyleFirstColumn = True
.ApplyStyleLastColumn = False
.ApplyStyleRowBands = True
.ApplyStyleColumnBands = False
End With
With wdApp.Selection
For x = 1 To 2
' set style name
.Style = "Heading 1"
.TypeText "Subject" & x
.TypeParagraph
.Style = "No Spacing"
For y = 1 To 20
.TypeText "paragraph text "
Next y
.TypeParagraph
Next x
' new paragraph
.TypeParagraph
' toggle bold on
.Font.Bold = wdToggle
.TypeText Text:="show some text in bold"
.TypeParagraph
'toggle bold off
.Font.Bold = wdToggle
.TypeText "show some text in regular front weight"
.TypeParagraph
End With
Some VBA vocabulary
TypeText
Inserts specified text at the beginning of the current selection. The selection is turned into an insertion point at the end of the inserted text.
If Options.ReplaceSelection = True then the original selection will be replaced. This behaves exactly the same as typing some text at the keyboard.
TypeParagraph
Insert a new blank paragraph. The selection is turned into an insertion point after the inserted paragraph mark. If Options.ReplaceSelection = True then the original selection will be replaced. This behaves exactly the same as pressing the Enter key.
output in MS Word:
Generating a Word table with VBA
'In Tools > References, add reference to "Microsoft Word XX.X Object Library" before running.
Dim wdApp As Word.Application
Dim wdDoc As Word.Document
Dim r As Integer
Set wdApp = CreateObject("Word.Application")
wdApp.Visible = True
Set wdDoc = wdApp.Documents.Add
wdApp.Activate
Dim wdTbl As Word.Table
Set wdTbl = wdDoc.Tables.Add(Range:=wdDoc.Range, NumRows:=5, NumColumns:=1)
With wdTbl
.Borders(wdBorderTop).LineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle
.Borders(wdBorderLeft).LineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle
.Borders(wdBorderBottom).LineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle
.Borders(wdBorderRight).LineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle
.Borders(wdBorderHorizontal).LineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle
.Borders(wdBorderVertical).LineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle
For r = 1 To 5
.Cell(r, 1).Range.Text = ActiveSheet.Cells(r, 1).Value
Next r
End With
output in MS Word:
Option Explicit
Dim wdApp As Word.Application
Sub extractToWord()
'In Tools > References, add reference to "Microsoft Word 12 Object Library" before running.
Dim lastCell
Dim rng As Range
Dim row As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim arrayOfColumns
arrayOfColumns = Array("", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "")
Dim thisRow As Range
Dim thisCell As Range
Dim myStyle As String
' get last cell in column B
lastCell = getLastCell()
Set rng = Range("B2:H" & lastCell)
'iterate through rows
For Each thisRow In rng.Rows
'iterate through cells in row row
For Each thisCell In thisRow.Cells
If thisCell.Value = arrayOfColumns(thisCell.Column) Or thisCell.Value = "" Then
' do nothing
''frWriteLine thisCell.Value, "Normal"
''frWriteLine arrayOfColumns(thisCell.Column), "Normal"
If thisCell.Value = arrayOfColumns(thisCell.Column) Or thisCell.Value = "" Then
End If
Else
myStyle = "Normal"
Select Case thisCell.Column
Case 2
myStyle = "Heading 1"
Case 3
myStyle = "Heading 2"
Case 4
myStyle = "Heading 3"
Case Is > 5
myStyle = "Normal"
End Select
frWriteLine thisCell.Value, myStyle
End If
arrayOfColumns(thisCell.Column) = thisCell.Value
Next thisCell
Next thisRow
End Sub
Public Function getLastCell() As Integer
Dim lastRowNumber As Long
Dim lastRowString As String
Dim lastRowAddress As String
With ActiveSheet
getLastCell = .Cells(.Rows.Count, 2).End(xlUp).row
End With
End Function
Public Function frWriteLine(someData As Variant, myStyle As String)
If wdApp Is Nothing Then
Set wdApp = New Word.Application
With wdApp
.Visible = True
.Activate
.Documents.Add
End With
End If
With wdApp
With .Selection
.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = wdAlignParagraphCenter
.Style = myStyle
.TypeText (someData)
.TypeParagraph
End With
End With
End Function
output in MS Word:

This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Word versions: 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003. If you are using a later version (Word 2007 or later), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for later versions of Word, click here: Creating a New Document in VBA.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated May 30, 2022)
This tip applies to Word 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003
One of the common things done during a macro is to create a new document. For instance, your macro could need the new document to hold processed text, or a different version of the document on which you are working.
To create a new document, simply include this line in your VBA macro:
Documents.Add
This creates a new document, based on Normal.Dot, adds it to the Documents collection, and makes the document active. This is the same as clicking the New button on the toolbar. If you want to create a new document based on a different template, simply use this command:
Documents.Add("MyTemplate.dot")
If you would like to know how to use the macros described on this page (or on any other page on the WordTips sites), I’ve prepared a special page that includes helpful information. Click here to open that special page in a new browser tab.
WordTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Word training.
(Microsoft Word is the most popular word processing software in the world.)
This tip (822) applies to Microsoft Word 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003. You can find a version of this tip for the ribbon interface of Word (Word 2007 and later) here: Creating a New Document in VBA.
Author Bio
With more than 50 non-fiction books and numerous magazine articles to his credit, Allen Wyatt is an internationally recognized author. He is president of Sharon Parq Associates, a computer and publishing services company. Learn more about Allen…
MORE FROM ALLEN
Disabling the Caps Lock Key
A few tips and tricks for working around the dratted Caps Lock button.
Discover More
Printing Row Numbers
On-screen Excel displays row numbers that help you easily see what is in each row. If you want to print these row …
Discover More
Word 2010 Styles and Templates (Table of Contents)
Styles are at the heart of Word’s formatting power. Understanding how to use styles can greatly increase your ability to …
Discover More
More WordTips (menu)
Saving a Document in a Macro
If you develop a macro to process your document, you may want the macro to save the document to disk. This is easily done …
Discover More
Jumping to the Start or End of a Document
When creating macros, it is often necessary to move the insertion point around the document so that text can be processed …
Discover More
Determining if Num Lock is On
Need to know if the Num Lock key is on or off? You can use a short bit of macro code to figure out the state of the key.
Discover More
Содержание
- 1 Add a word document
- 2 Close a document
- 3 Generating Word ata from an Excel VBA program
- 4 Load contact table from Access and create letter in Word
- 5 Open an Existing Document
- 6 Save a document
- 7 Save Changes to a Document
- 8 To close a specific document, you can close the active document or you can specify a document name:
- 9 To create a new document that uses a specific template, use this:
- 10 To save a document with a new name, use the SaveAs method
Add a word document
<source lang="vb">
Sub wordDoc()
Dim WordApp As Object
Set WordApp = CreateObject("Word.Application")
With WordApp
.Documents.Add
End With
End Sub
</source>
Close a document
<source lang="vb">
Sub exitFor()
Dim Doc As Document
For Each Doc In Documents
If Doc.Name = "Document1" Then Exit For
Doc.Close
Next Doc
End Sub
</source>
Generating Word ata from an Excel VBA program
<source lang="vb">
Sub MakeMemos()
Dim WordApp As Object
Set WordApp = CreateObject("Word.Application")
For i = 1 To 3
Application.StatusBar = "Processing Record " & i
SaveAsName = ThisWorkbook.Path & "test.doc"
With WordApp
.Documents.Add
With .Selection
.Font.Size = 14
.Font.Bold = True
.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = 1
.TypeText Text:="M E M O R A N D U M"
.TypeParagraph
.TypeParagraph
.Font.Size = 12
.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = 0
.Font.Bold = False
.TypeText Text:="Date:" & vbTab & Format(Date, "mmmm d, yyyy")
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText Text:="To:" & vbTab & " Manager"
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText Text:="From:" & vbTab & _
Application.userName
.TypeParagraph
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText "text"
.TypeParagraph
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText Text:="Units Sold:" & vbTab & "asdf"
.TypeParagraph
.TypeText Text:="Amount:" & vbTab & Format(1000, "$#,##0")
End With
.ActiveDocument.SaveAs FileName:=SaveAsName
.ActiveWindow.Close
End With
Next i
WordApp.Quit
Set WordApp = Nothing
Application.StatusBar = ""
MsgBox " memos were created and saved in " & ThisWorkbook.Path
End Sub
</source>
Load contact table from Access and create letter in Word
<source lang="vb">
Sub ControlWord()
Dim objWord As New Word.Application
Dim rsContacts As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim strLtrContent As String
rsContacts.ActiveConnection = CurrentProject.Connection
rsContacts.Open "tblContacts"
objWord.Documents.Add
Do While Not rsContacts.EOF
strLtrContent = rsContacts("FirstName") & " " & rsContacts("LastName")
strLtrContent = strLtrContent & rsContacts("Address") & vbCrLf
strLtrContent = strLtrContent & rsContacts("City") & ", " & rsContacts("Region")
strLtrContent = strLtrContent & " " & rsContacts("PostalCode")
strLtrContent = strLtrContent & "Dear " & rsContacts("FirstName") & " "
strLtrContent = strLtrContent & rsContacts("LastName") & ":"
objWord.Selection.EndOf
objWord.Selection.Text = strLtrContent
objWord.Selection.EndOf
objWord.Selection.InsertBreak
rsContacts.MoveNext
Loop
objWord.Visible = True
objWord.PrintPreview = True
End Sub
</source>
Open an Existing Document
<source lang="vb">
Sub Main()
Dim wdApp As Word.Application Set wdApp = GetObject(, "Word.Application") wdApp.Documents.Open Filename:="C:Arrays.docx", ReadOnly:=True, AddtoRecentFiles:=False
End Sub
</source>
Save a document
<source lang="vb">
Sub WordLateBound()
Dim objWord As Object
Dim objDoc As Object
Set objWord = CreateObject("Word.Application")
Set objDoc = objWord.Documents.Add
objDoc.SaveAs "C:testdoc2.doc"
objDoc.Close
Set objDoc = Nothing
Set objWord = Nothing
End Sub
</source>
Save Changes to a Document
<source lang="vb">
Sub main()
Dim wdApp As Word.Application Set wdApp = GetObject(, "Word.Application") wdApp.Documents.Save
End Sub
</source>
To close a specific document, you can close the active document or you can specify a document name:
<source lang="vb">
Sub main()
Dim wdApp As Word.Application
Set wdApp = GetObject(, "Word.Application")
wdApp.ActiveDocument.Close
"or
wdApp.Documents("Arrays.docx").Close
End Sub
</source>
To create a new document that uses a specific template, use this:
<source lang="vb">
Sub add()
Dim wdApp As Word.Application Set wdApp = GetObject(, "Word.Application") wdApp.Documents.Add Template:="Contemporary Memo.dot"
End Sub
</source>
To save a document with a new name, use the SaveAs method
<source lang="vb">
Sub Main()
Dim wdApp As Word.Application Set wdApp = GetObject(, "Word.Application") wdApp.ActiveDocument.SaveAs "C:MemoTest.docx"
End Sub
</source>